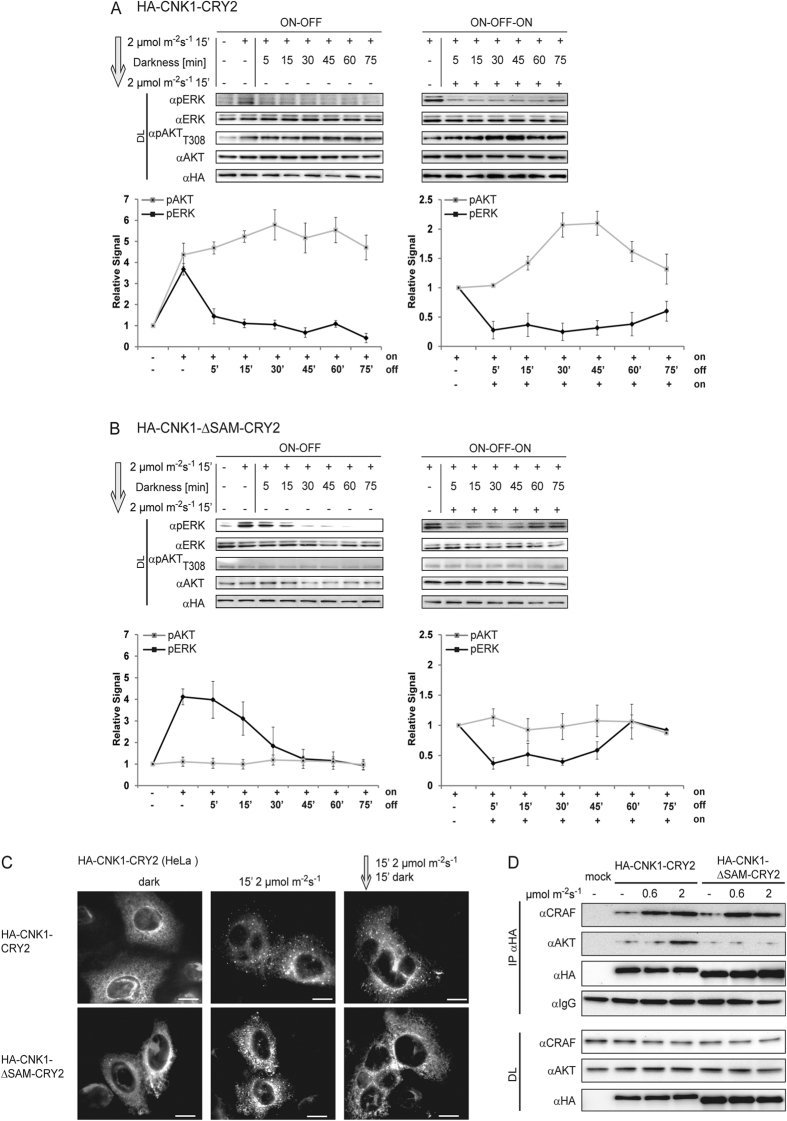
Figure 3. The SAM domain of CNK1-CRY2 is essential for mediating the AKT/RAF crosstalk.
(A) ON-OFF (left) and ON-OFF-ON (right) kinetics of HA-CNK1-CRY2 activated by illumination with 460 nm and 2 μE m−2 s−1 for the time points indicated monitored by ERK and AKT phosphorylation. Charts represent quantification of pERK and pAKT immunoblot data of three independent experiments. (B) ON-OFF (left) and ON-OFF-ON (right) kinetics of HA-CNK1ΔSAM-CRY2 activated by illumination with 460 nm and 2 μE m−2 s−1 for the time points indicated monitored by ERK and AKT phosphorylation. Charts represent quantification of pERK and pAKT immunoblot data of three independent experiments. (C) Immunostaining of HA-CNK1-CRY2 and HA-CNK1ΔSAM-CRY2 overexpressed in HeLa cells demonstrated that the presence of the SAM domain delayed dissociation of CNK1-CRY2 clusters induced by illumination with 460 nm and 2 μE m−2 s−1 for 15 min. Left: anti-HA antibody for HA-CNK1-CRY2 and HA-CNK1ΔSAM-CRY2, middle: DAPI for nuclear staining, right: merge images (Red: anti-HA antibody; Blue: DAPI), scale bar: 10 μm. (D) HEK293T cells expressing HA-CNK1-CRY2 and HA-CNK1ΔSAM-CRY2 were light-stimulated as indicated. Deletion of the SAM domain abolished binding of AKT to CNK1 but did not affect binding of CRAF to CNK1.