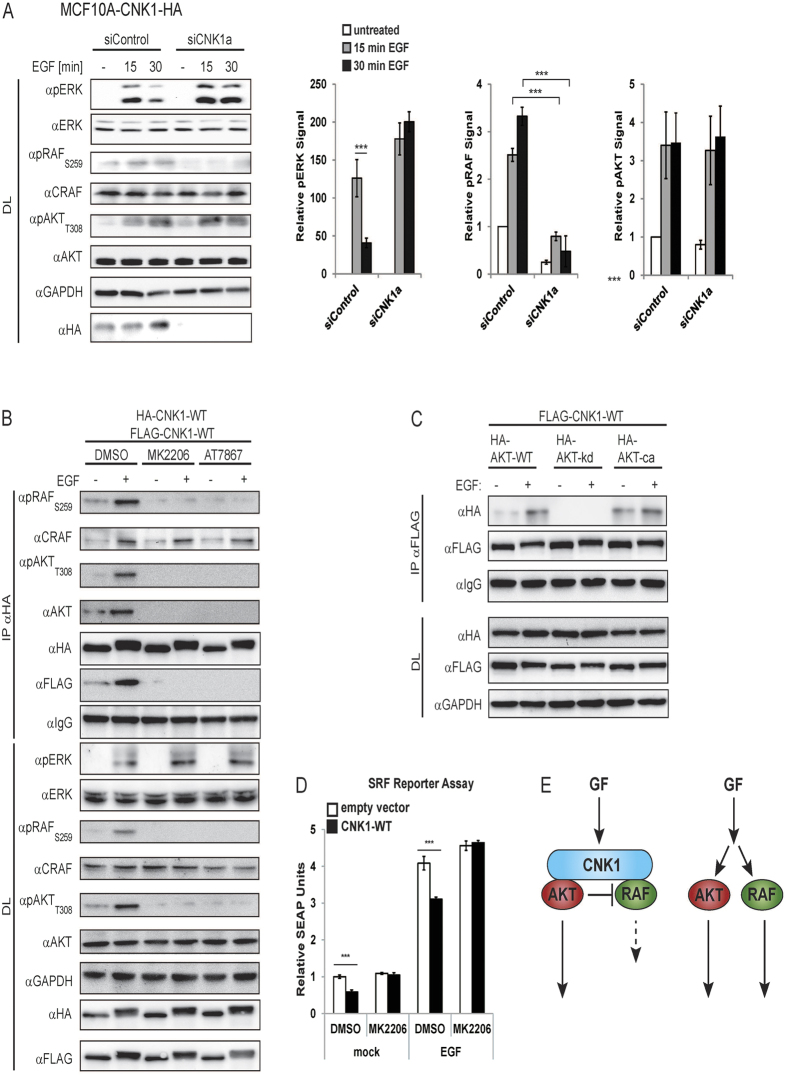
Figure 5. CNK1 mediates AKT-dependent inhibition of CRAF.
(A) Knockdown of CNK1 in MCF10A-CNK1-HA cells abrogates AKT-dependent inhibitory phosphorylation of CRAF at Ser259 leading to increased ERK phosphorylation in EGF (20 ng/ml) stimulated cells. Bar charts represent quantified signals of three independent experiments. N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, ***p < 0.001. See also Supplementary Figure S3. (B) Treatment of HEK293T cells with the AKT inhibitors MK2206 or AT7867 abolished EGF (20 ng, 15 min)-induced binding of AKT and pT308AKT to CNK1 and also their residual interaction found in non-stimulated cells. (C) Wildtype AKT (HA-AKT-WT) and a constitutively active AKT mutant (HA-AKT-ca) bound to CNK1 in EGF-treated cells whereas a kinase-defective AKT mutant (HA-AKT-kd) failed to interact with CNK1. (D) Inhibition of AKT (MK2206) increased CNK1-induced SRF-dependent reporter gene expression (SEAP). N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, ***p < 0.001. See Supplementary Figure S8 for control of protein expression. (E) Scheme of the CNK1 mediated AKT/RAF crosstalk.