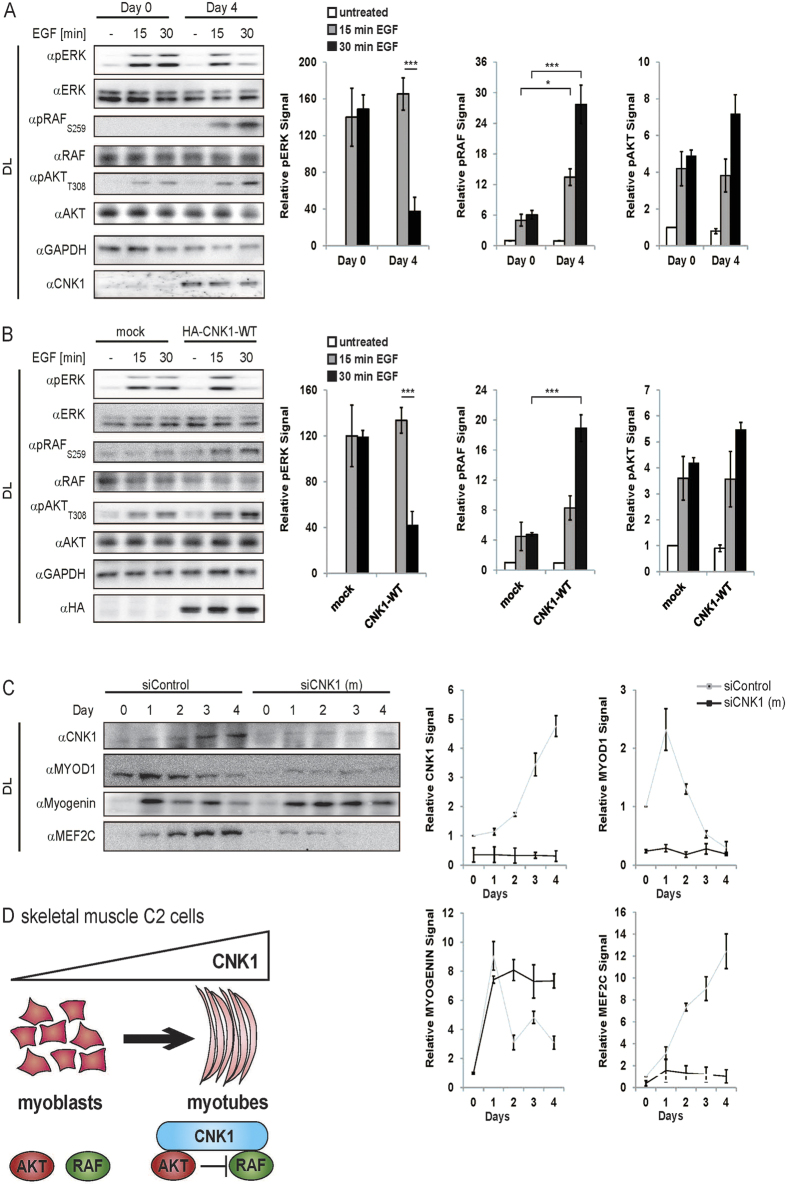
Figure 7. CNK1 is a differentiation marker promoting skeletal muscle cell differentiation.
(A) EGF (20 ng/ml) stimulates phosphorylation of ERK in proliferating C2 myotubes (day 0). In differentiated C2 cells (day 4) EGF led to transient phosphorylation of ERK since activated AKT inhibits RAF monitored by phosphorylation of Ser259. Bar charts represent quantified data of three independent experiments. N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (B) Expression of CNK1 in C2 myoblasts constitutes the AKT/RAF crosstalk as shown by increased AKT activity, increased inhibitory RAF Ser259 phosphorylation and transient ERK phosphorylation. Bar charts represent quantified data of three independent experiments. N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, ***p < 0.001. (C) Expression of CNK1 is induced in mouse C2 skeletal muscle cells and knockdown of CNK1 interferes with the expression of transcription factors used as differentiation markers. Quantification of CNK1 and transcription factor expression in siRNA and siControl-treated C2 cells is shown. Data obtained from three independent experiments. (D) Scheme showing that induction of CNK1 expression enables the AKT/RAF crosstalk controlling differentiation of C2 skeletal muscle cells.