Figure 4.
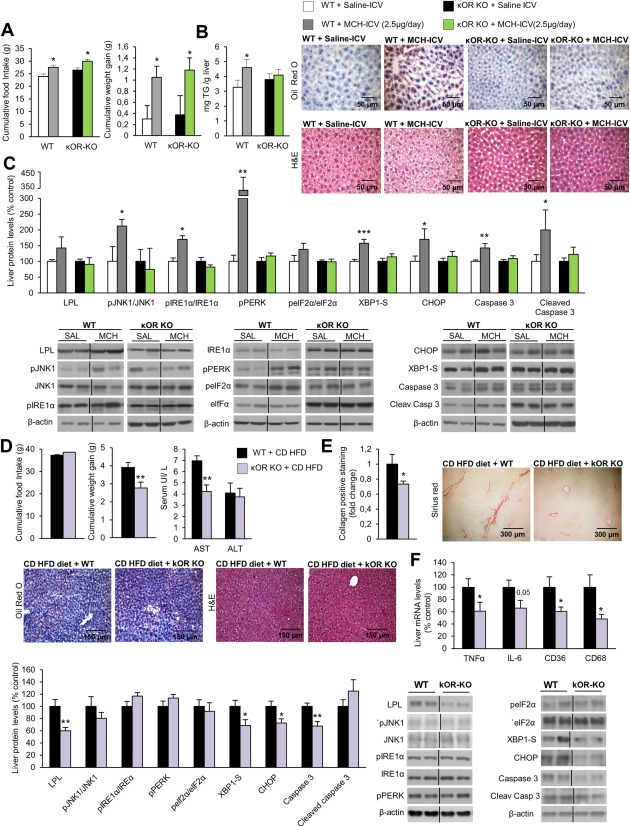
κOR‐KO mice are resistant to MCH‐induced and CD‐HFD–induced liver damage. Effect of a 7‐day ICV MCH infusion (2.5 µg/day) in either WT or κOR‐KO mice fed a chow diet on food intake and body weight (A); TG liver content and oil red O and hematoxylin and eosin liver section staining represented in the microphotographs (B); and liver protein levels of LPL, pJNK, JNK, pIRE1α, IRE1α, pPERK, peIF2α, eIF2α, XBP1S, CHOP, caspase 3, and cleaved caspase 3 (C). Effect of CD‐HFD (2 weeks) in WT and κOR‐KO mice on food intake and body weight, serum levels of AST, and ALT (D); collagen‐positive staining and representative photomicrograph of liver sections with sirius red, oil red O, and hematoxylin and eosin staining (E); liver protein levels of LPL, pJNK1, JNK1, pIRE1α, IRE1α, pPERK, peIF2α, eIF2α, XBP1S, CHOP, caspase 3, and cleaved caspase 3 and hepatic gene expression of TNFα, IL6, CD36, and CD68 (F). Protein β‐actin levels were used to normalize protein levels. Dividing lines indicate splicings within the same gel. Separated photos indicate that gels were run independently. Values are mean ± standard error of the mean of 7‐10 animals per group. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 versus controls. Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; SAL, saline.
