Figure 1.
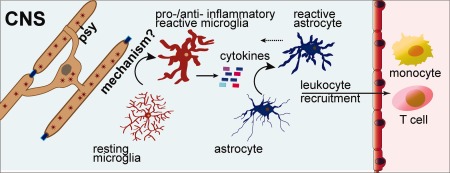
Model of innate immune response in KD. Loss of GALC enzymatic activity causes oligodendrocyte dysfunction (see also Fig. 2), which is sensed by microglia through an unknown mechanism to trigger their reactivation. Reactive microglia release cytokines and other immune signaling molecules that activate astrocytes and recruit peripheral leukocytes. Depending on the stage of the disease, reactive glia could provide either pro‐ or anti‐inflammatory effects, and the actions of innate immune signals influence disease progression.
