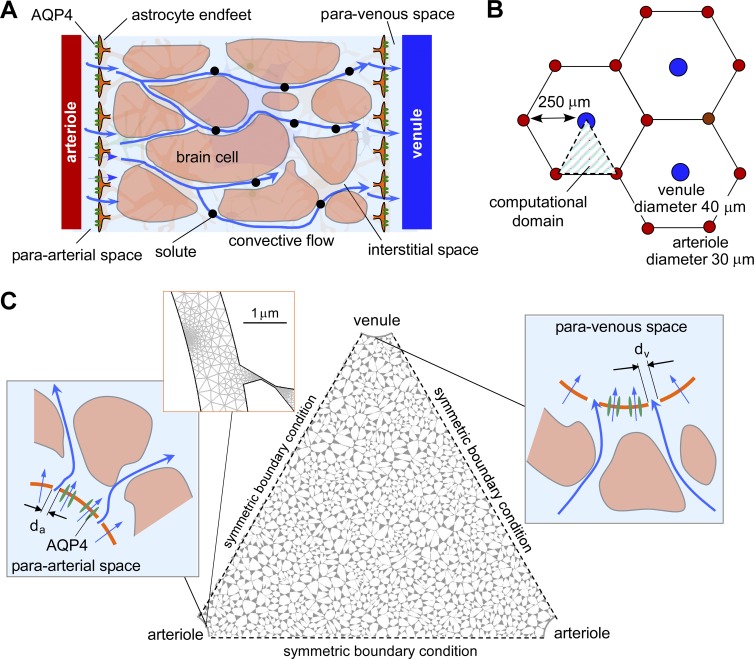
Figure 1.
Spatial model of convective fluid movement from para-arterial to paravenous spaces in brain ECS. (A) Schematic showing the major features of the proposed glymphatic mechanism, including convective fluid movement from para-arterial to paravenous spaces through brain extracellular (interstitial) space. (B) Hexagonal spatial arrangement of arterioles and venules in brain parenchyma, showing triangular computational domain. (C) Diagram of water and solute movement between the para-arterial space and ECS, and the ECS and the paravenous space. da and dv, gap distances between astrocyte endfeet in para-arterial and paravenous space.