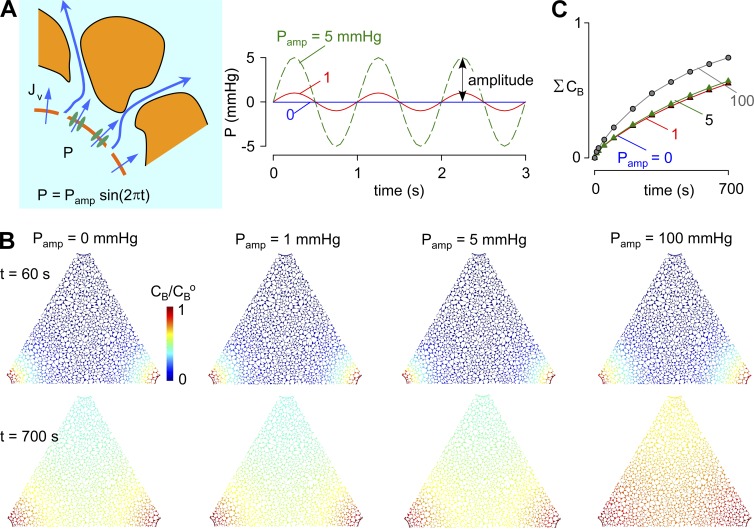
Figure 6.
Influence of pulsatile pressure in the para-arterial space on solute movement in brain ECS. (A, left) Schematic showing hydrostatic pressure driven in the para-arterial space water transport across the astrocyte endfoot barrier; (right) para-arterial pressure waveform of amplitude Pamp and frequency 1 Hz. (B) Pseudocolored images showing tracer solute accumulation in the ECS, as in Fig 3, for different Pamp. Parameters: Pf = 0.04 cm/s, D = 10−10 m2/s, and α = 0.2. (C) Kinetics of tracer solute accumulation in ECS for the indicated Pamp.