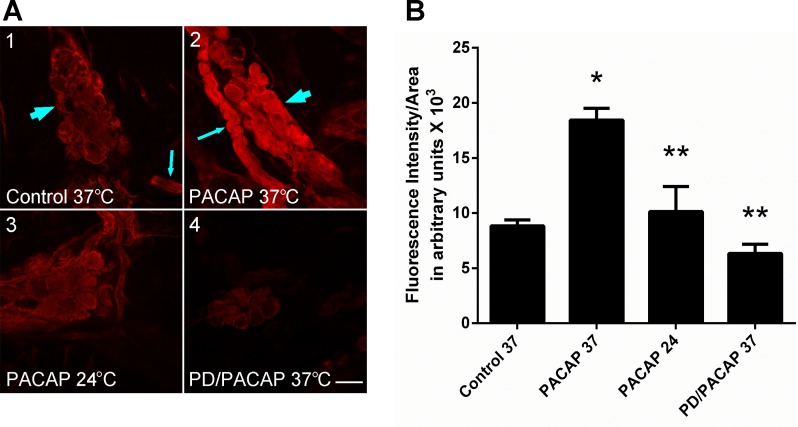
Fig. 2.
PACAP stimulates phosphorylated ERK (pERK) generation in guinea pig cardiac neurons. A: confocal images (∼1-μm optical sections) of cardiac ganglia neurons processed for pERK immunoreactivity and visualization using a Cy3-conjugated secondary antiserum. A1: control cardiac ganglia preparation maintained at 37°C prior to fixation. Arrowhead points to cardiac ganglion containing multiple neurons with only basal pERK immunoreactivity; arrow points to a nerve bundle surrounded by pERK-immunoreactive Schwann cells. A2: cardiac ganglia preparation exposed to 25 nM PACAP at 37°C for 20 min prior to fixation. Arrow points to a nerve bundle surrounded by pERK-immmunoreactive Schwann cells; arrowhead points to a cardiac ganglion containing multiple neurons with increased pERK immunoreactivity. A3: cardiac ganglia preparation exposed to 25 nM PACAP at 24°C for 20 min prior to fixation. Neuronal PACAP-stimulated pERK levels were attenuated, consistent with blockade of endosomal signaling at room temperature. A4: cardiac ganglia preparation pretreated with the MEK inhibitor PD 98059 (50 μM) for 15 min and then exposed to 25 nM PACAP + PD 98059 at 37°C for 20 min prior to fixation. MEK inhibition blocked PACAP-stimulated ERK activation. Calibration bar = 20 μm. B: averaged fluorescence intensity per area for conditions shown in A. Results were averaged from ≥3 cardiac ganglia whole mount preparations. Control 37, control at 37°C (54 cells in 3 whole mount preparations); PACAP 37, PACAP at 37°C (61 cells in 4 whole mount preparations); PACAP 24, PACAP at 24°C (60 cells in 3 whole mount preparations); PD/PACAP, PD 98059 + PACAP at 37°C (47 cells in 3 whole mount preparations). *Significantly different from control 37. **Significantly different from PACAP 37.