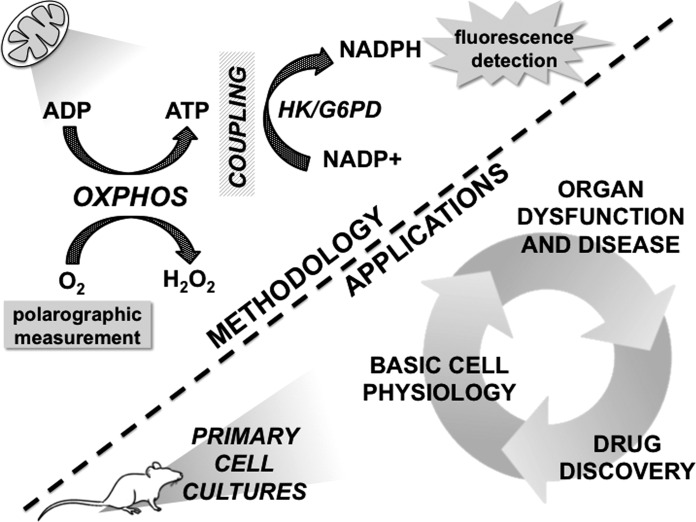
Fig. 1.
The technique employed by Lark et al. for high-resolution measurement of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) efficiency in permeabilized skeletal muscle fiber bundles (top), and potential applications in primary cell cultures from other organ systems (bottom). OXPHOS efficiency is defined as the molar ratio of ATP produced to O2 consumed. Enzymatic coupling of ATP as substrate for NADH+ reduction to NADPH allows real-time quantification of ATP via NADPH fluorescence, while O2 consumption is simultaneously measured polarographically. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; HK, hexokinase; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; O2, molecular oxygen.