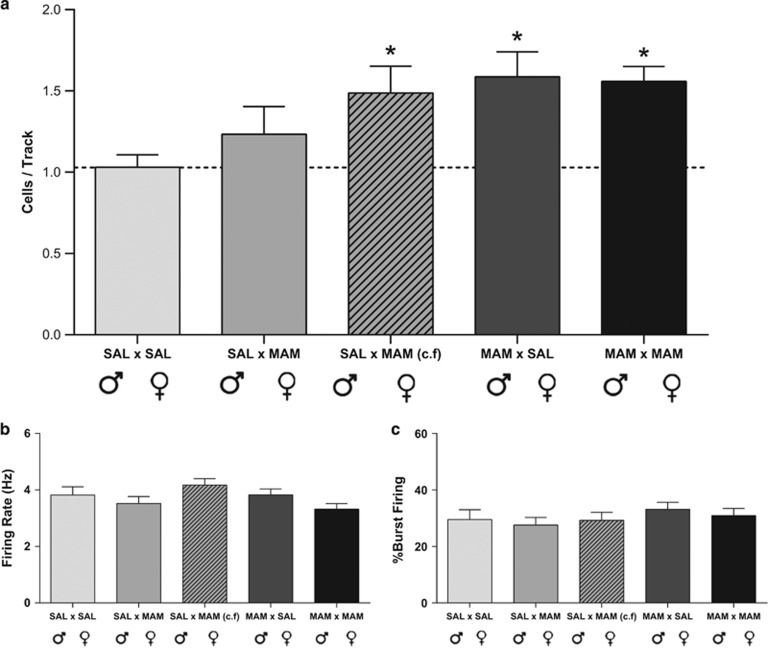
Figure 2.
Offspring born from methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM)-treated parents exhibit enhanced ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine neuron activity. F2 generation rats born from MAM-treated fathers, regardless of the phenotype of the mother, display a significant increase in dopamine neuron population activity (a) when compared with F2 rats born from saline parents. Cross-fostered (c.f., dashed bar) rats born from MAM-treated mothers, but raised by control dams, also demonstrated an increase in dopamine neuron population activity. No significant differences were observed in the firing rate (b) or burst firing (c) of dopamine neurons between any crosses. *represents a significant difference from saline (♂) × saline (♀).