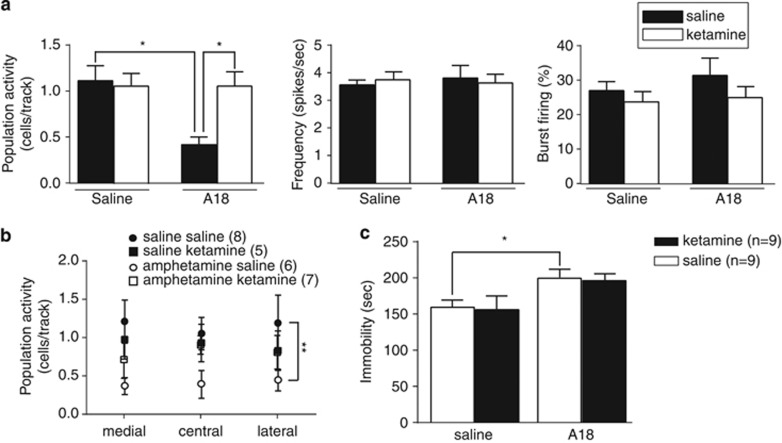
Figure 4.
Ketamine reverses the amphetamine-induced decrease in DA neuron population activity to levels comparable to saline rats without affecting the increased immobility in the FST. (a) The number of spontaneously active DA neurons per electrode track (left), firing rate (middle), and burst firing (right). The amphetamine-induced decrease in DA neuron population activity is reversed to levels comparable to saline rats by injection of ketamine. (b) This restoration of activity occurred across the medial–lateral extent of the VTA. (c) In contrast, ketamine did not alter the amphetamine withdrawal-induced increase in the immobility time in the modified forced swim test and did not affect immobility in saline rats. Error bars are±SEM. *p<0.05.