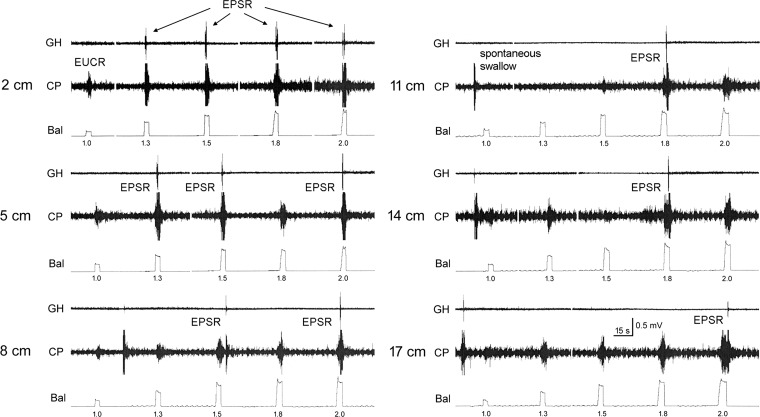
Fig. 1.
The effect of balloon distension of the esophagus. These are recordings of geniohyoideus (GH) and cricopharyngeus (CP) electromyography (EMG) during esophago-upper esophageal sphincter (UES) contractile reflex (EUCR) or esophagus-stimulated pharyngeal swallow response (EPSR) in response to distensions of the esophagus at various esophageal locations. The EUCRs are associated with increased CP EMG, and the EPSRs are associated with increased GH and CP EMG activated in a sequential fashion. Note that only 1 EPSR was activated per stimulus, and the delays between stimulus and EPSR were variable. EPSRs were more likely to occur at higher distensions and at more rostral esophageal locations of the stimulus. Occasionally, spontaneous swallows occurred between stimuli. Bal, balloon. Balloon distensions were 1.0–2.0 cm in diameter of a 3-cm-long balloon in the esophagus at 2–17 cm from the CP.