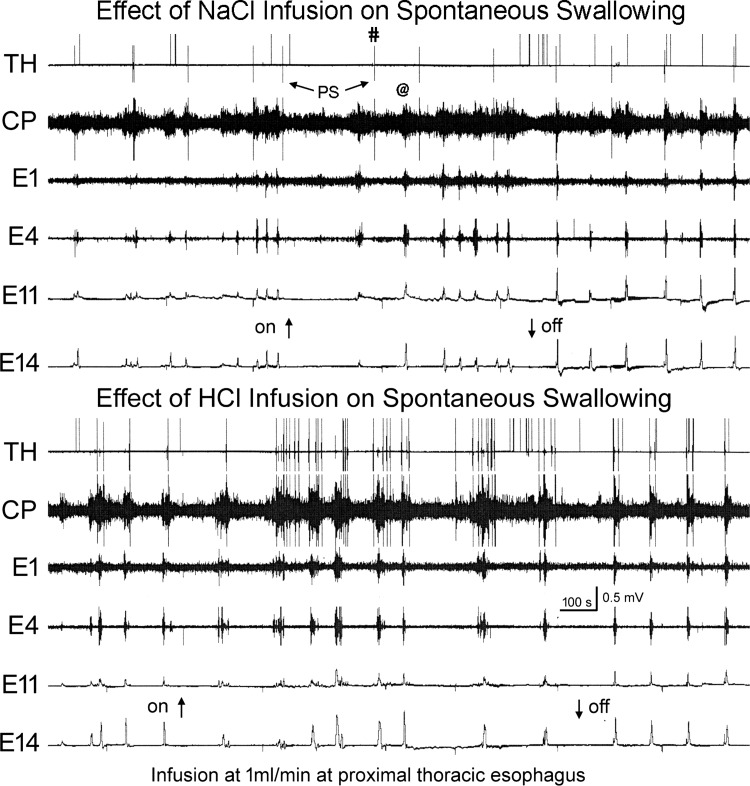
Fig. 4.
Comparison of the effects of NaCl and HCl on rate of spontaneous pharyngeal swallows (PS). These are TH, CP, E1, and E4 EMG recordings and E11 and E14 manometric recordings in response to fluid infusion, NaCl or HCl, into the proximal thoracic esophagus (8 cm from the CP). Note that HCl, but not NaCl, infusion significantly increased the rate of spontaneous pharyngeal swallows. The pharyngeal swallows are indicated by the increased TH and CP EMG in a sequential fashion. Not all pharyngeal swallows were accompanied by esophageal peristalsis (#), and not all esophageal peristalses were accompanied by pharyngeal swallows (@).