Figure 1.
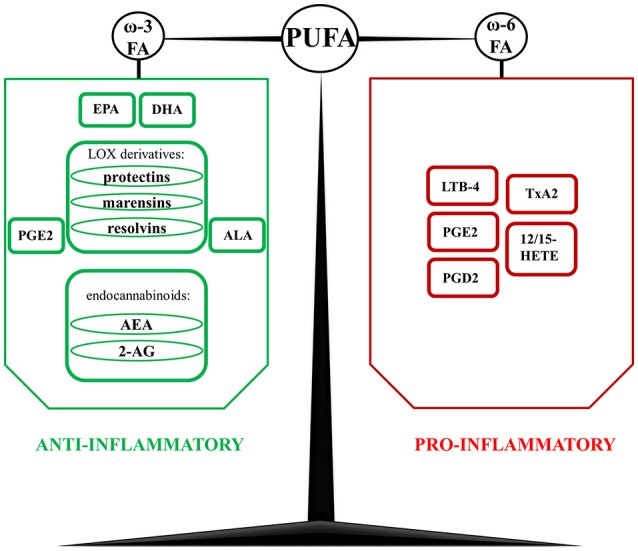
Derivatives of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) with anti- and pro-inflammatory properties. In contrast to n-3 PUFA-derived mediators, which are mostly considered as anti-inflammatory, n-6 PUFA derivatives promote inflammatory response. However, one of the unique metabolites of n-6 PUFA are lipoxins (Lx)- LxB4 and LxB5, which display a wide spectrum of anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution actions. AA, arachidonic acid; AEA, N-arachidonoylethanolamide, anandamide; ALA, alpha-linoleic acid; 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; FA, fatty acid; LOX, lipoxygenases; LTB-4, leukotriene B-4; LxA4, lipoxin A4; LxB4, lipoxin B4; PGD2, prostaglandin D2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TxA2, thromboxane A2; 12/15 HETE, 12/15 hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid.
