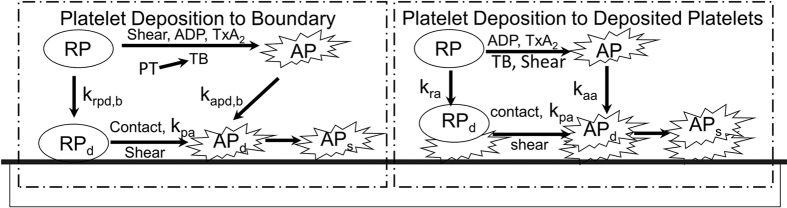
Figure 1. Schematic depiction of the thrombosis model, comprised of platelet deposition, aggregation, and stabilization.
RP: resting platelet, AP: activated platelet, RPd and APd: deposited resting and active platelets, APs: stabilized deposited active platelets. Agonists that cause activation (RP to AP) are adenosine diphosphate, ADP; thromboxane A2, TxA2; shear, and thrombin, TB – which is synthesized from prothrombin (PT). The suffix b refers to the reaction with the boundary (surface). The constants kpa, kra, kaa, krpd,b, kapd,b, refer to the reaction rates for inter-conversion of the associated platelet states.