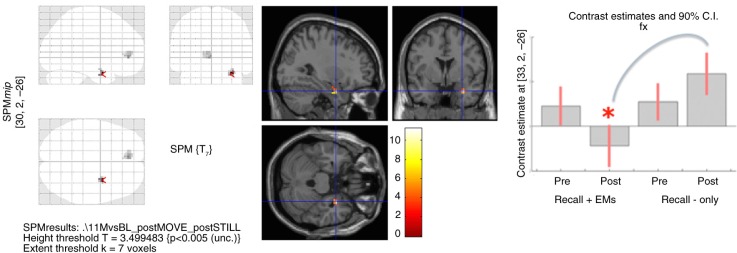
Fig 1.
Full-factorial analysis of the script-driven imagery (see Table 2), showing on the left panel: the glass brain with decreased right amygdala and rostral ACC activity post-“recall with EMs” compared with post-“recall-only”; on the middle panel: T-values of decreased right amygdala activity; and on the right panel: contrast estimates in the right amygdala per time and condition: decreased right amygdala activity post-“recall with EMs” compared with post-“recall-only.” Applying regions-of-interest (ROI) analyses, we used an explicit mask, consisting of the bilateral mask of the amygdala, DLPFC, rostral ACC, DMPFC, anterior insula, and visual cortex (see Methods for detailed information). Images were set at a threshold of p-uncorrected <0.005 for multiple comparisons and k≥5 for illustrative purposes.