Fig. 10.
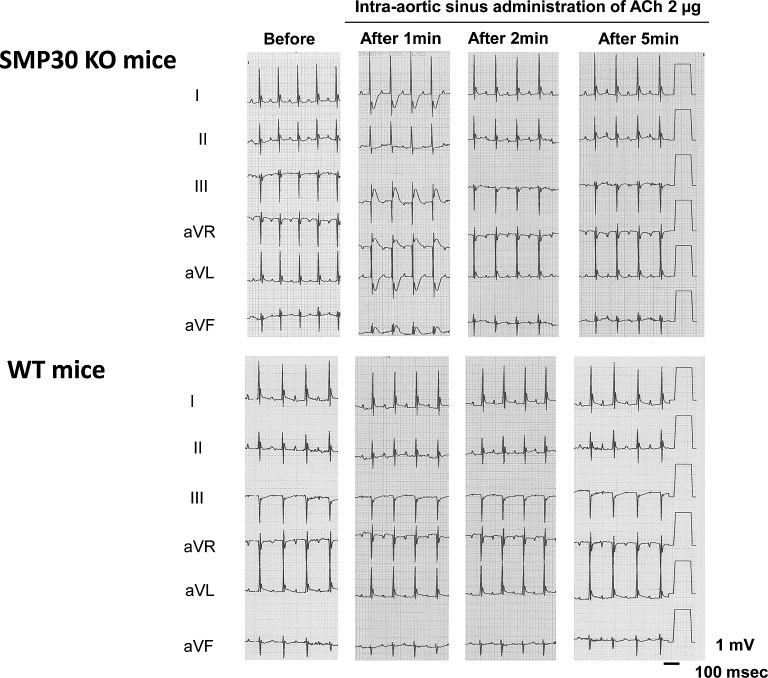
The intra-aortic sinus administration of acetylcholine (ACh, 2 µg) to SMP30 knockout mice induced transient ST-T segment elevation and reciprocal ST-T segment depression in the electrocardiograms. In the wild mice, the ACh-induced ST-T segment change did not appear. Before administration: before the administration of ACh, after 1, 2, and 5 min; 1, 2, and 5 min after the intra-aortic sinus administration of ACh.
