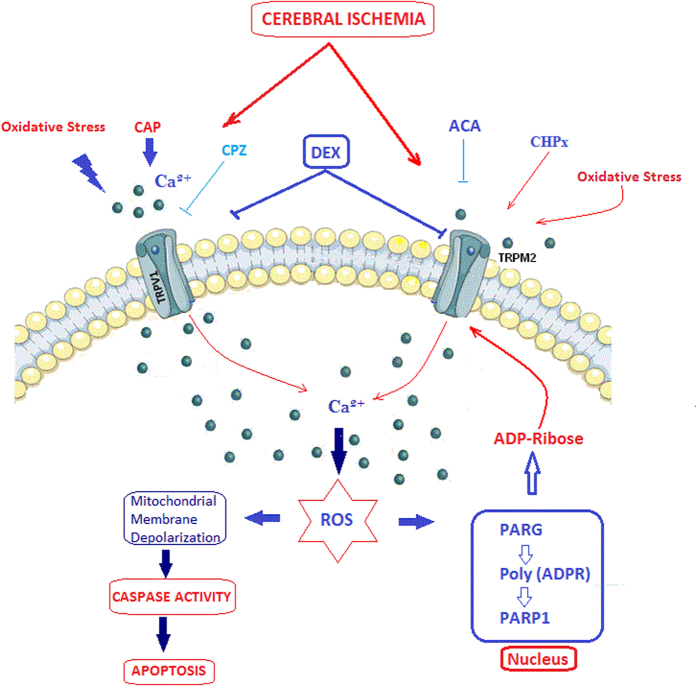
Figure 8. Possible molecular pathways of involvement of DEX in cerebral ischemia-induced apoptosis, oxidative stress and calcium accumulation through TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in the HIPPO and DRG neurons of rats.
The TRPM2 channel is activated by ADP-ribose (ADPR) and oxidative stress although it is inhibited by ACA. The TRPV1 channel is activated by oxidative stress and capsaicin (CAP) and it is blocked by capsazepine (CPZ). Increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration through TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in cerebral ischemia (ISC) may lead to neuronal toxicity, reactive oxygen species (ROS), inflammatory processes and eventual cell death. DEX reduced oxidative stress, apoptotic factors (including caspase 3 and 9), mitochondrial membrane depolarization and Ca2+ influx through the inhibition of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channel activation.