Fig. 3.
Significant contribution of TCM with Th17 and Th1Th17 phenotypes to the pool of HIV DNA reservoir.
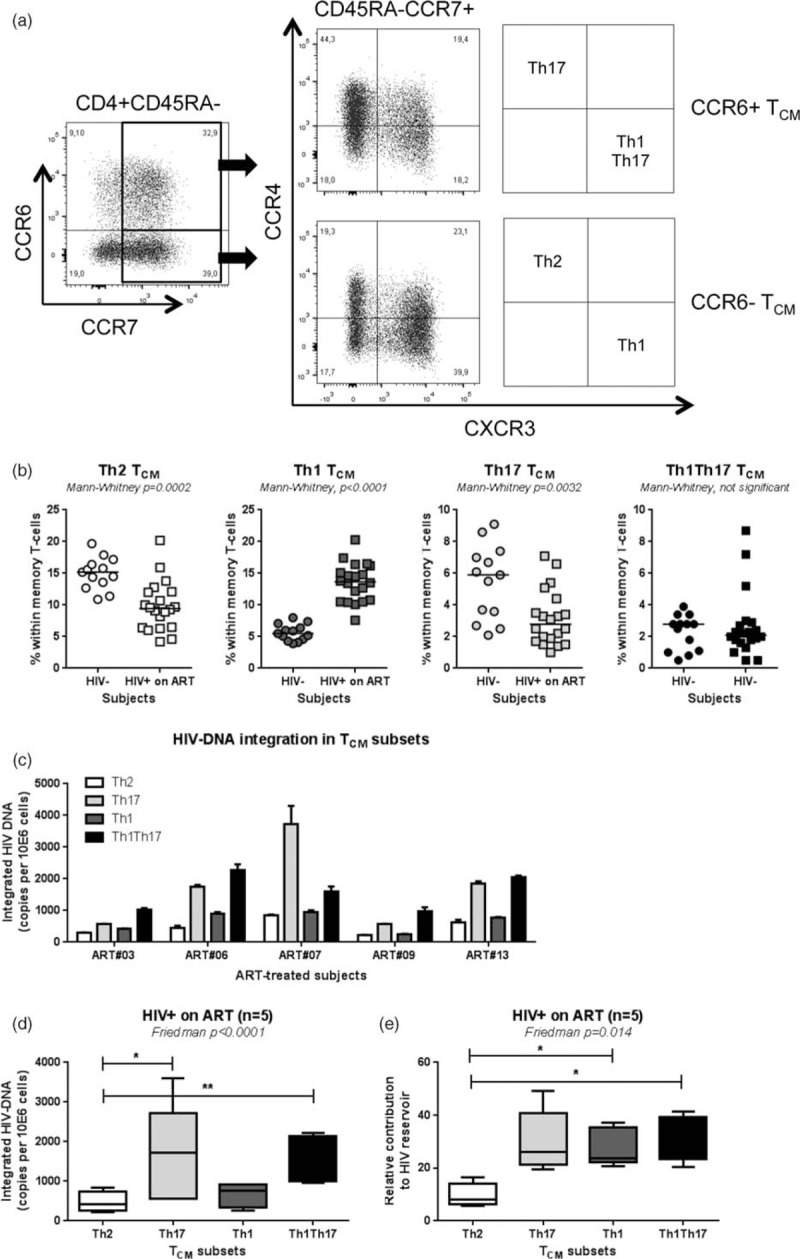
ART, antiretroviral therapy; TCM, central memory T cell. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell from HIV+ on ART and HIV individuals were stained with a cocktail of CD3, CD4, CD45RA, CCR6, CCR4, CCR7, and CXCR3 Abs. (a) Shown is the gating strategy for the identification of TCM cells with Th17 (CCR6+CCR4+CXCR3−), Th1Th17 (CCR6+CCR4−CXCR3+), Th2 (CCR6−CCR4+CXCR3−), and Th1 (CCR6−CCR4−CXCR3+) phenotypes. The frequency of the four TCM subsets was compared between HIV+ on ART and HIV− controls (b). Highly pure TCM subsets were sorted by flow cytometry from HIV+ on ART individuals (Suppl. Figure 3) and integrated HIV DNA levels were quantified. Shown are levels of integrated HIV DNA in subsets from n = 5 individual donors (c) and statistical analysis in all donors (d). The relative contribution of the four TCM subsets to the pool of integrated HIV DNA within TCM cells was calculated considering the frequency of each subset as described in Fig. 2f legend. (e). Indicated in the graphs are Mann-Whitney (b) and Friedman and Dunn's multiple comparison test P values (∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001) (d and e).
