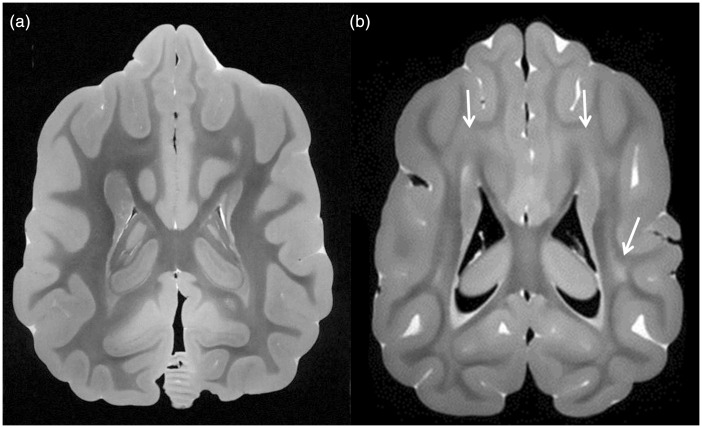
Figure 3.
Comparison of white matter in a normal canine brain and a canine affected by Krabbe disease. (a) Axial B0 image from diffusion imaging sequence (essentially a T2-weighted image) from the normal canine shows dark signal throughout white matter, extending up to the subcortical regions, consistent with normal myelination. (b) Axial B0 image from the Krabbe brain shows large regions of hyperintense signal within deep white matter and subcortical white matter (arrows), consistent with impaired myelination, in a pattern that is similar to that of humans with markedly progressed Krabbe disease.