Figure 1.
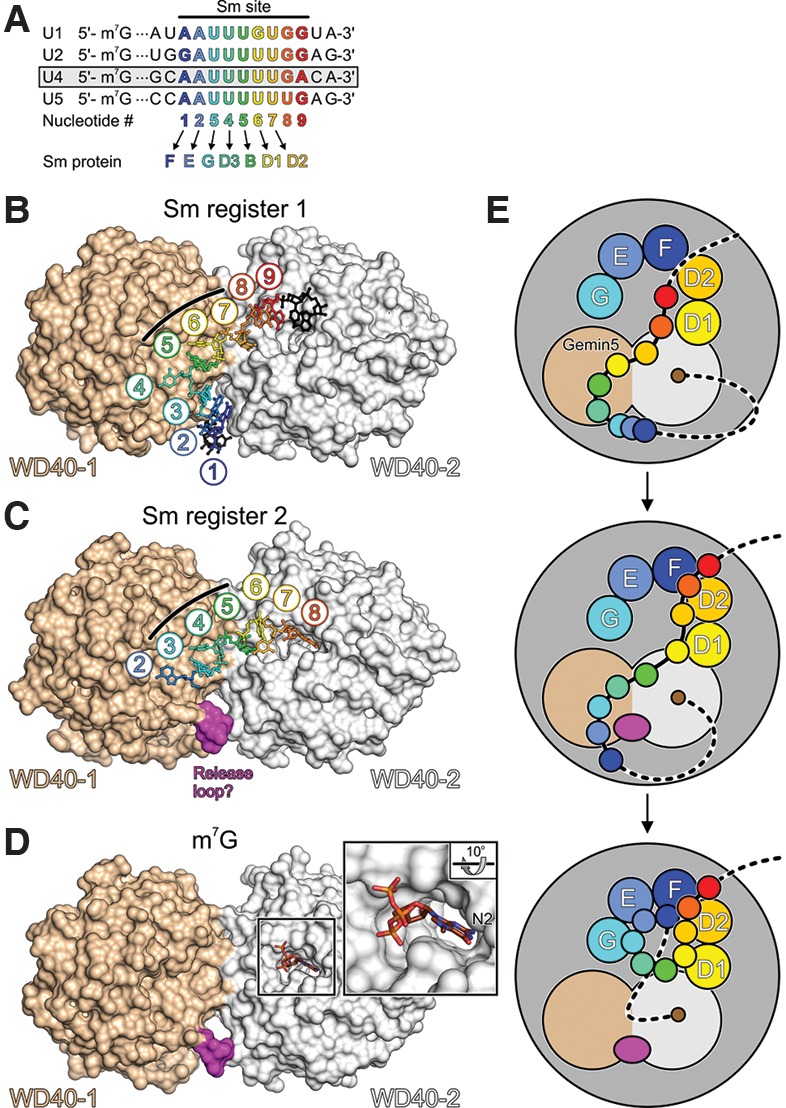
Possible role of Gemin5 in UsnRNP assembly. (A) Alignment of the Sm sites and neighboring nucleotides of the major spliceosomal U1, U2, U4, and U5 snRNAs. U4 snRNA, used in the present studies, is boxed. Sm site nucleotides are numbered 1–9 and colored blue to red in a 5′-to-3′ direction. Sm proteins F, E, G, D3, B, D1, and D2 are assembled on nucleotides 1–7 of the Sm sites to form Sm cores. (B,C) Structures of the Gemin5 N-terminal tandem WD40 domains in complex with a 13-nucleotide (nt) (B) and a 7-nt (C) oligomer containing a complete or partial Sm site, respectively (based on Jin et al. 2016). The two RNA molecules bind with different registers across a positively charged concave surface formed by both WD40 domains. Three consecutive uridines (U5, U6, and U7 or U3, U4, and U5 of the Sm site) bind in an analogous manner and at identical pockets to the center of the protein (black lines). Nucleotides 3′ of U7 in B lack extensive contacts to the protein. U8 in C occupies a pocket on the second WD40 domain that also accommodates the m7G cap (see D). (D) Binding of an m7GpppG mimic of a 5′-capped snRNA to a pocket on the second WD40 domain (based on Xu et al. 2016). The second guanine base is disordered in the structure. (Close-up) N2 of m7G is buried in the pocket. An m2,2,7G cap bearing two additional methyl groups on N2 could not be accommodated due to the disruption of hydrogen bonds and steric hindrance. (E) Model for the role of Gemin5 in Sm core assembly. Gemin5 could bind snRNAs concomitantly via the m7G cap and the Sm site. Nucleotides 3′ of a Sm site would be free to engage in initial contacts to the partially assembled Sm proteins on the SMN complex. A shift in the register of Sm site binding on Gemin5 could feed Sm site nucleotides 6 and 7 into their binding pockets on D1 and D2, respectively. The shift in register could involve a loop of the first WD40 domain occupying a position where Sm site nucleotides 1–3 are initially bound on Gemin5. After subsequent handover of Sm site nucleotides 1, 2, and 3 to Sm proteins F, E, and G, respectively, Gemin5 might still hold onto the cap, protecting it from hypermethylation until the D3–B heterodimer has been assembled on Sm site nucleotides 4 and 5. After assembly of the Sm core has been completed, another handover of the cap from Gemin5 to the cap methyltransferase TGS1 would have to occur in this scenario.
