Figure 1.
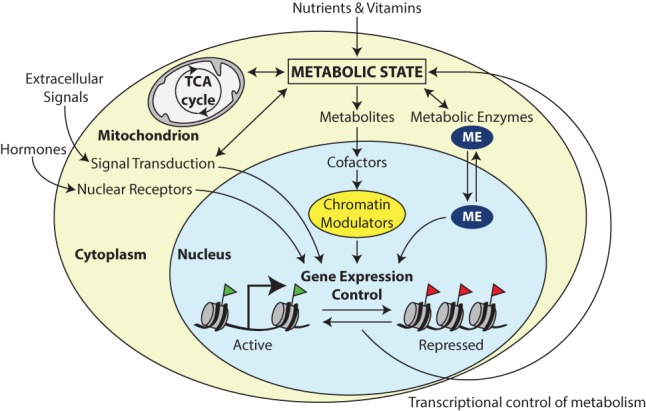
The interface between metabolism and transcription. Specialized transcription factors that are activated by metabolic sensors or extracellular signals, such as hormones, direct a transcriptional response to changes in metabolic state. In addition, key components of intermediary metabolism are cofactors or cosubstrates of chromatin-modifying enzymes. Therefore, changes in cofactor availability may affect chromatin structure and gene expression. Finally, specialized metabolic enzymes (MEs) do double duty as regulators of chromatin and transcription. Frequently, cytoplasmic–nuclear partitioning is used as a regulatory mechanism to link metabolic state to transcriptional outcomes.
