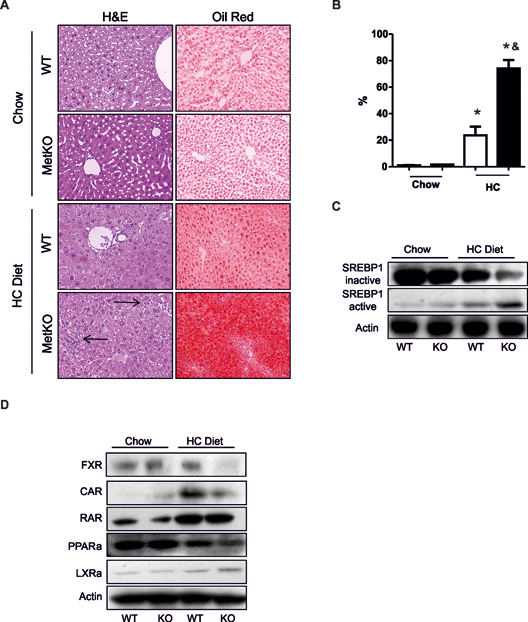
Fig. 2.
High-cholesterol diet induces steatohepatitis and affects major nuclear receptors and lipogenic-related factors. A: hematoxylin & eosin and Oil red O staining on paraffin liver sections from MetKO or WT mice fed the high-cholesterol (HC) diet or control chow diet. Original magnification, X200. Arrows show inflammatory infiltration. Images are representatives of at least four animals for each group. B: Quantification of fat accumulation. * p < 0.05 vs WT chow diet; & p< 0.05 vs WT high-cholesterol (HC) diet. C: Activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1). D: Western blots of nuclear receptors related to lipid and bile acids metabolism: Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR), Constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), Retinoid Acid Receptor (RAR), Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), and Liver X Receptor alpha (LXRα). Images are representative of at least three independent experiments. Actin was used as a loading control.