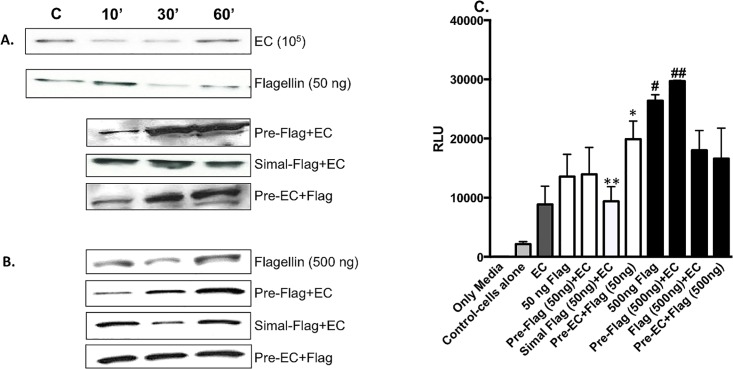
Fig 3. Flagellin and E. coli O83:H1 induced differential degradation of IkB-alpha and NF-κB activation via TLR5.
Western blot analysis detected IkB-alpha degradation in IECs as follows: (A) IECs stimulated with EC alone, 50 ng of flagellin or various combination of both stimuli. (B) IECs were stimulated with the same stimulus regime as in (A) except using 500 ng of flagellin. (C) The results showed that NF-κB activation was modest in cells stimulated with EC while NF-κB activation was higher in cells stimulated with 50 ng of flagellin alone compared to EC alone. Pre-EC+Flag [50ng] functioned synergistically to induce significant NF-κB activation compared to Simal-EC+flagellin [50ng], EC or flagellin [50ng] alone (*p<0.05). NF-κB activation was significantly lower in the Simal-EC+flagellin [50ng] compared to 50 ng of flagellin alone, Pre-Flag [50ng]+EC and Pre-EC+Flag [50ng] (**p<0.05). A 10-fold increase in its dose to 500 ng induced significant NF-κB activation compared to 1 x 105 of EC (# p<0.05). NF-κB activation was maximal in cells stimulated with 500 ng of flagellin prior to EC (Pre-Flag [500ng]+EC) compared to Simal+Flag [500 ng]+EC or Pre-EC+Flag [500 ng] (## p<0.05).