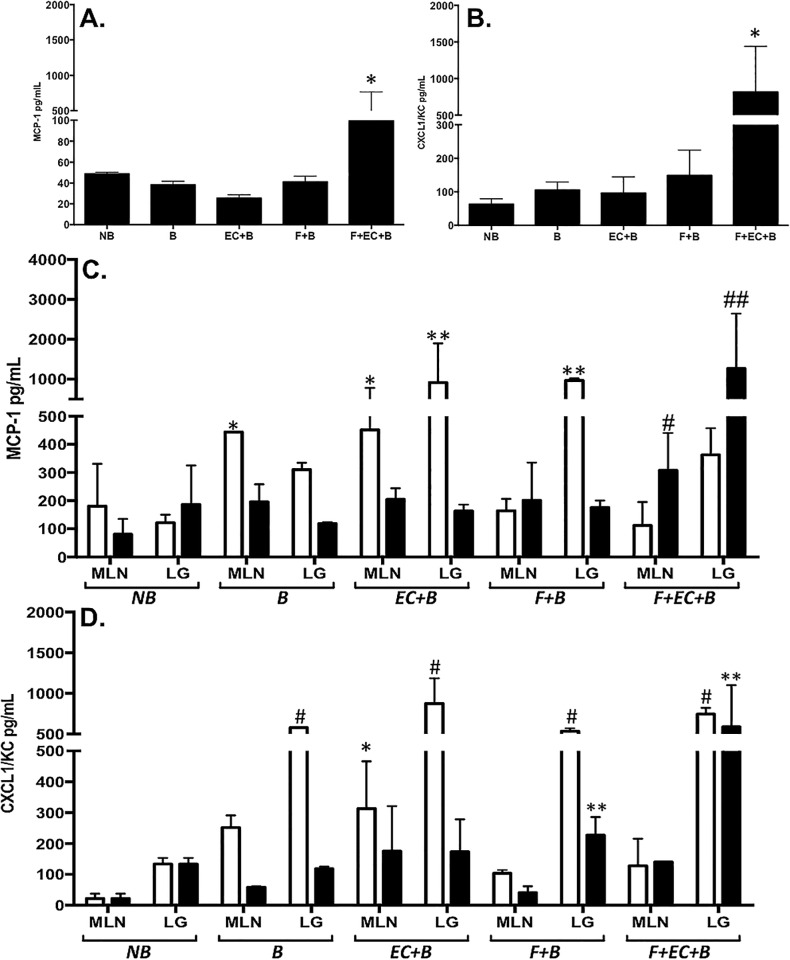
Fig 6. Intraluminal flagellin and E. coli O83:H1 synergistically induced systemic cytokine production following burn injury.
Mice were gavaged with 5 ug of flagellin and/or 1 X 105 CFU EC 2h prior to burn. Animals were humanely euthanized at 24 (white bars) or 48h (black bars) post-burn and serum (A and B), MLNs and lungs (C and D) were collected and analyzed for MCP-1 (A and C) and CXCL1/KC (B and D) by ELSIA. Groups are as described in the methods and results including sham, non-burned controls (NB), 30% TBSA injury (B), EC and 30% TBSA (B+EC), 5ug flagellin and 30% TBSA (B+F) and the gavaged combination of EC and flagellin prior to burn (B+F+EC). Data are represented as mean±SEM from at least 5 animals in a group. Comparisons with statistically different values are denoted as follows: (A & B) MCP-1 and CXCL1/KC were significantly higher in the serum of the B+EC+F group vs. all other groups (*p<0.01). (C) MCP-1 was significantly higher in the MLNs of B and B+EC at 24h compared to NB (*p<0.05). MCP-1 was significantly elevated in the lungs of B+EC and B+F groups at 24h compared to B lungs (**p<0.05). B+EC+F induced maximal levels of MCP-1 in the MLNs and lungs at 48h vs. all other groups (#p<0.05). (D) CXCL1/KC was significantly higher in the lungs of all groups compared to non-burned (#p<0.05). CXCL1/KC was significantly higher in the MLNs of B+EC mice compared to all other groups (*p<0.01). B+F and B+EC+F groups had significantly higher levels of CXCL1/KC in the lungs at 48h vs. all other groups (**p<0.05).