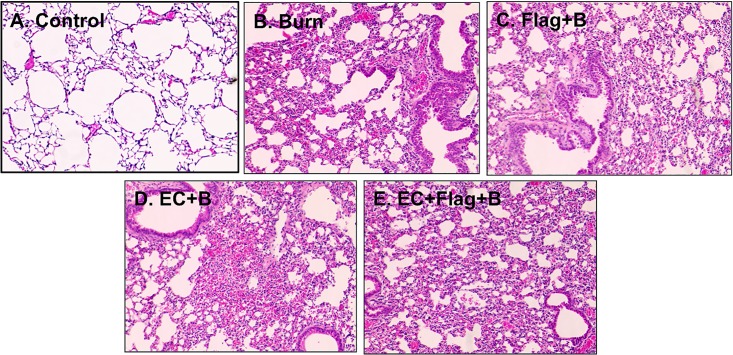
Fig 7. Intraluminal flagellin and E. coli O83:H1 synergistically induced lung damage following burn injury.
Lungs were collected at 48h post-burn from mice as described in Fig 6. Compared to normal, healthy controls (A) significant cell infiltration and disruption of the alveolar structure was observed in mice receiving burn, flagellin and burn, EC and burn, or all three insults (B-D). All three insults also induced intra-alveolar hemorrhaging and prominent cell accumulation indicated lung parenchymal injury (E). Mag 20X.