Figure 2.
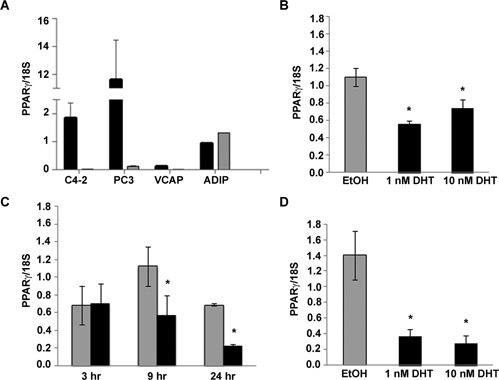
The androgen DHT reduces PPARγ mRNA in AR‐positive cells. (A) qRT‐PCR was used to detect basal levels of total PPARγ and PPARγ2 mRNA in total RNA samples from human prostate cancer cell lines and adipose tissue RNA. The amount of PPARγ mRNA in each sample was normalized to 18S rRNA. Black bars represent the normalized amount of total PPARγ (PPARγ1 and PPARγ2) while the gray bars represent PPARγ2 mRNA. (B) C4‐2 cells were treated with EtOH or different concentrations of DHT for 24 h. Total RNA was then isolated from treated cells. The amount of PPARγ mRNA and 18S rRNA in each RNA sample was measured using qRT‐PCR. (C) C4‐2 cells were treated with EtOH (gray bars) or 1 nM DHT (black bars) for 3–24 h. PPARγ mRNA and 18S rRNA levels in each sample were then measured using qRT‐PCR. (D) VCaP cells were treated for 24 h with either EtOH or increasing concentrations of DHT. The level of PPARγ and 18S RNA in treated cells was then measured by qRT‐PCR. In parts A–D, each bar represents the mean ± SEM of three independent samples. *P < 0.05 compared to EtOH group.
