Figure 3.
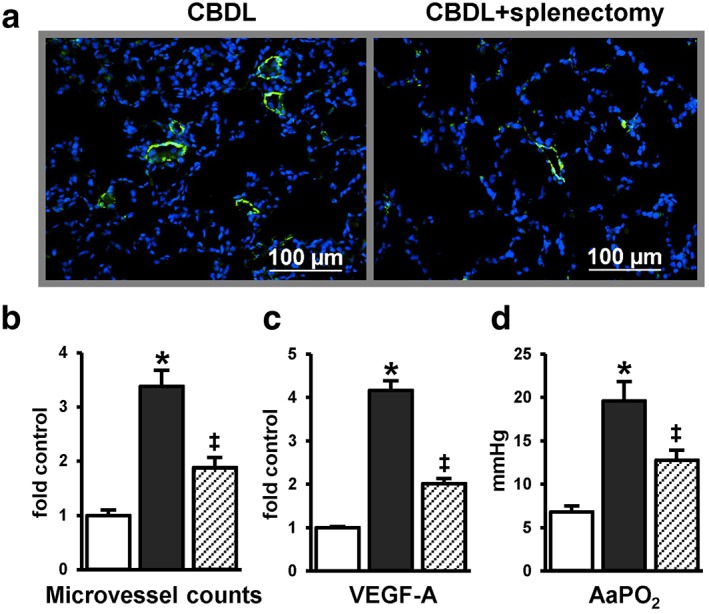
The effects of spleen removal on pulmonary angiogenesis and gas exchange in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lung microvessels were stained by Factor VIII (in green) and counted in common bile duct ligation (CBDL) animals with or without splenectomy. (a) Representative immunofluorescent images of Factor VIII; (b) quantitation of Factor VIII‐stained microvessels; (c) graphical summaries of lung vascular endothelial growth factor‐A (VEGF‐A) mRNA levels; and (d) arterial gas exchange was assessed by the alveolar–arterial oxygen gradient (AaPO2). Splenectomy significantly decreased lung microvessel numbers and VEGF‐A levels and improved AaPO2 after CBDL. Values are expressed as means ± SE (n = 6–8 animals for each group). *
P < 0.05 compared with sham. ‡
P < 0.05 compared with CBDL.  , control;
, control;  , CBDL;
, CBDL;  , CBDL + splenectomy.
, CBDL + splenectomy.
