Figure 1.
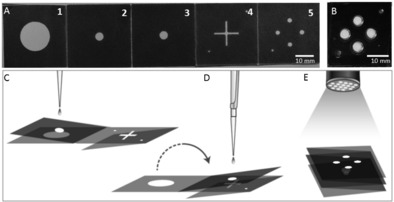
Paper‐based multiplexed LAMP detection of malaria in blood. A) Foldable paper devices: Dark areas are printed with hydrophobic wax. The device consists of five panels (1–5) folding onto each other, and a plastic cover for LAMP processing to avoid evaporation (B). The design also incorporates alignment marks on two corners (in the bottom left and top right corners) to assign the results. C) Illustrates the extraction process. Panels 2 and 3 are folded together and onto Panel 1. The sample is dispensed onto the device (panel 3) and extracted using capillary flows vertically (flow of liquid from Panel 3 to Panel 1). By folding the device (flipping the Panel 2–3 fold onto Panels 4 and 5), the sample is transferred to the LAMP spots (D) where the reaction is carried out. The signal is read out using a UV flashlight (365 nm; E).
