Figure 13.
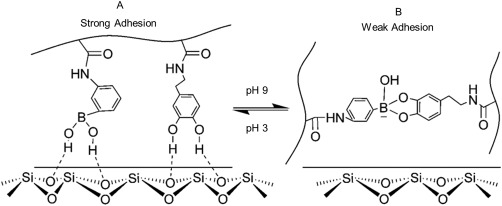
Schematic representation of the smart adhesive containing catechol and phenylboronic acid functional groups. At an acidic pH, both the catechol and borate functional groups contributed to strong interfacial binding with the wetted borosilicate substrate (A). In a basic pH, formation of catechol–boronate complexation reduced the interfacial binding strength of the adhesive (B). Changing the pH, effectively converts the smart adhesive between its adhesive and non‐adhesive states. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 226, Copyright 2016 American chemical society.
