Figure 4.
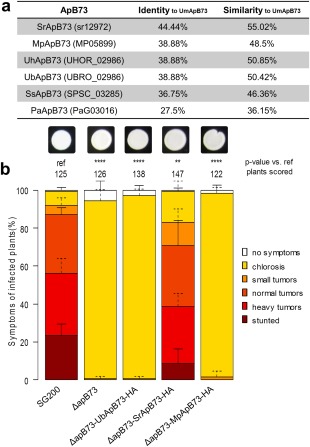
ApB73 has orthologues in other smut fungi. (a) Identity and similarity values of ApB73 orthologues from different smut fungi to the ApB73 protein from Ustilago maydis. Included here are protein sequences from Sporisorium reilianum, Melanopsichium pennsylvanicum, Ustilago hordei, Ustilago bromivora, Sporisorium scitamineum and Pseudozyma aphidis. Values were calculated using amino acid sequences and feeding them into the software tool SIAS (Immunomedicine Group, 2015). (b) Disease ratings of different complementation strains of the ΔapB73 mutant. The mutant strain SG200ΔapB73 was transformed with a construct expressing UbApB73, SrApB73 or MpApB73 under the native ApB73 promoter. Seedlings of maize cv. B73 were infected 7 days after germination and scored for symptoms at 12 days post‐infection (dpi). In the top row, photographs of the respective strains are shown after growth on filamentation‐inducing charcoal plates for 24 h. Disease scores are shown on the right. The mean values of three independent infections are depicted and the total number of infected plants is indicated above the respective columns. The mean and standard deviation of relative counts from replicates are displayed. For clarity, only positive error bars are shown. P values were calculated by Fisher's exact test. Multiple testing correction was performed using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001.
