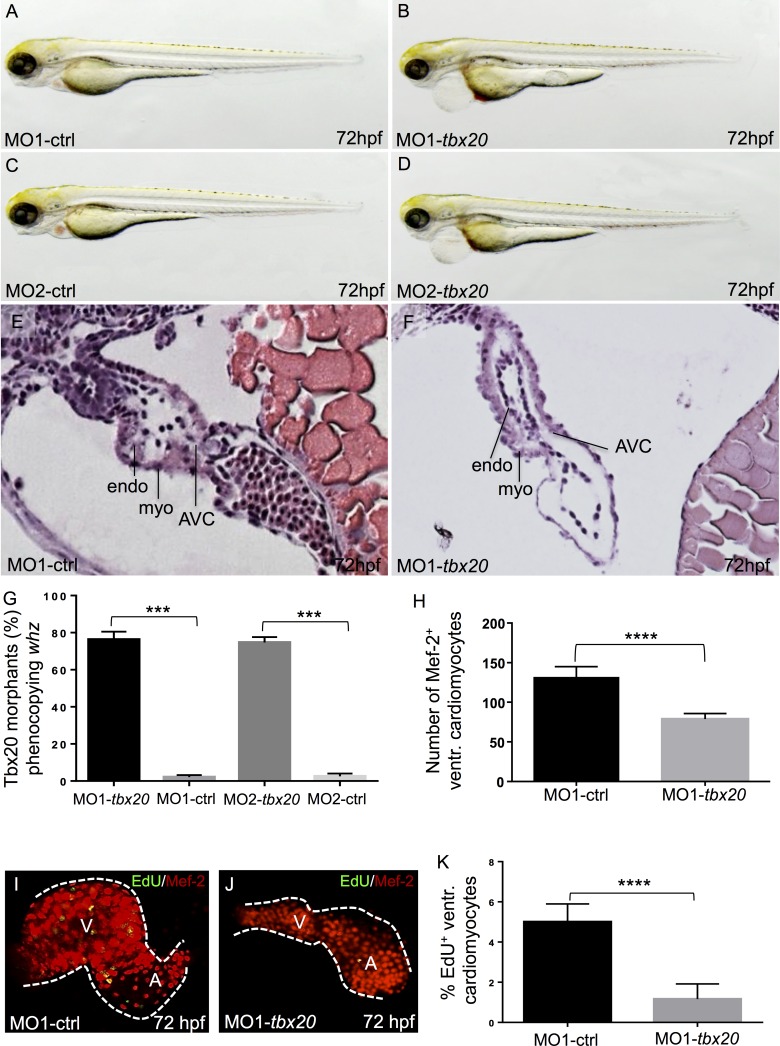
Fig 4. Knock-down of zebrafish tbx20 phenocopies the whz mutant phenotype.
(A-D) Lateral view of wild-type embryos injected with zebrafish tbx20-specific control Morpholinos (MO-ctrl) (A, C) and tbx20 start and splice Morpholinos (MO-tbx20) (B, D) at 72 hpf, respectively. Knock-down of tbx20 phenocopies the whz mutant phenotype, whereas injection of the same amount of specific-control Morpholinos does not affect heart growth. (E, F) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of sagittal histological sections of MO-ctrl (E) and MO-tbx20 (F) injected hearts at 72 hpf. In contrast to control hearts, tbx20 morphant ventricles appear small and the myocardium monolayered. (G) 78% (MO1-tbx20) and 76% (MO2-tbx20) of the injected embryos are indistinguishable from whz mutant embryos. (H) Tbx20 morphant hearts show significantly reduced ventricular cardiomyocytes at 72 hpf (MO1-control: 130.7±10 SD, MO1-tbx20: 86.5±10 SD, n = 10; p = 0.0001). (I-K) Cardiomyocyte proliferation in Tbx20 morphant ventricles is significantly reduced compared to controls at 72 hpf (MO1-control: 6±2% SD, MO1-tbx20: 1±2% SD, n = 10; p = 0.0001).