Figure 4.
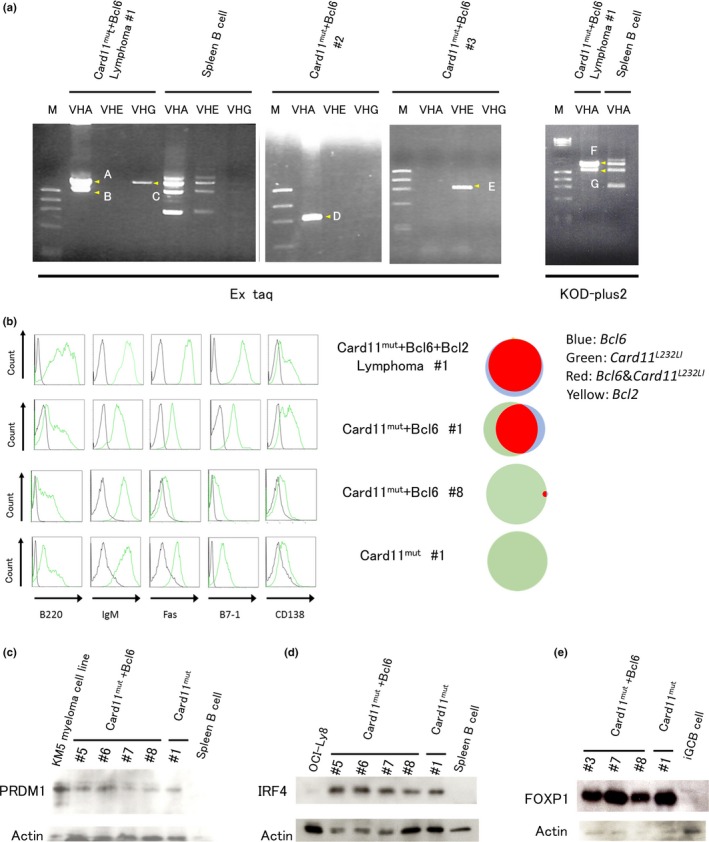
Clonality and properties of lymphomas. (a) Immunoglobulin heavy chain genes amplified by PCR from genomic DNA of lymphoma cells using combinations of VHA/VHE/VHG (forward) and JH4 intron (reverse) primers. PCR products amplified by Ex Taq or by KOD‐plus2 were fractionated by gel electrophoresis and bands were marked by A–E and F–G, respectively (yellow arrowheads). These amplified products were cloned into a plasmid vector and sequenced. Amplified products from genomic DNA of normal, non‐transduced spleen B cells were also electrophoresed as a control, to show their polyclonal status. M, markers. (b) Phenotype of the developed lymphoma cells as assessed by flow cytometry. Cells in the developed lymphoma were analyzed for the expression of the indicated molecules by flow cytometry (left). Control samples are represented by black lines. The fractions of cells that expressed each surrogate marker of transduced genes (GFP, Card11 L232 LI; hCD4, Bcl6; hCD8, Bcl2) of the corresponding tumor samples are represented by the Venn diagram (right). (c–e) Expression of PR domain 1 (PRDM1) (c), interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) (d), and forkhead box P1 (FOXP1) (e) in developed lymphoma, as detected by Western blotting.
