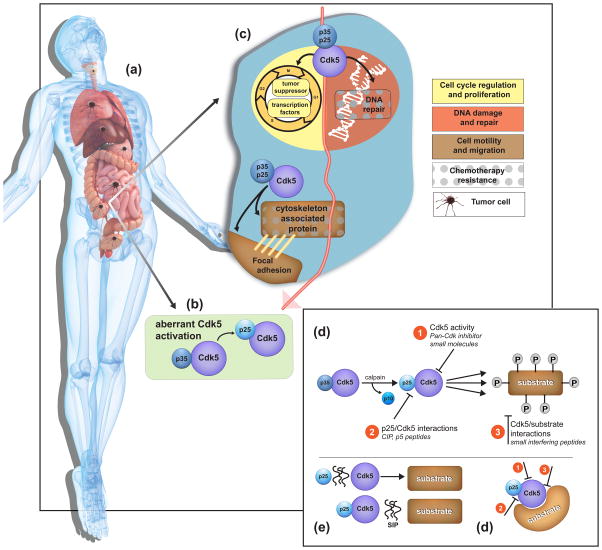
Figure 1 – Key Figure. Targeting Cdk5 in cancer.
(a) Cdk5 contributes to carcinogenesis in several organs throughout the body. (b) Cdk5 activation is dependent on its binding to the cofactor, p35, or its proteolytic cleavage product, p25 (green box). (c) At a cellular level, Cdk5 is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and cell proliferation by phosphorylating tumor suppressors and transcription factors, and in the DNA damage response upon exposure to genotoxic agents such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Cdk5 plays a role in cell motility and migration by regulating the cytoskeleton and focal adhesions. The role of Cdk5 in the DNA damage response and cytoskeleton remodeling has been linked to resistance to common chemotherapies. Therapeutic targeting of Cdk5 is achieved either by 1) inhibiting Cdk5 kinase activity with a pan-Cdk inhibitor or small molecules (d); by 2) preventing Cdk5 binding to p25 using peptides (e); or by 3) interfering with Cdk5 association and phosphorylation of its substrate using peptides (f).