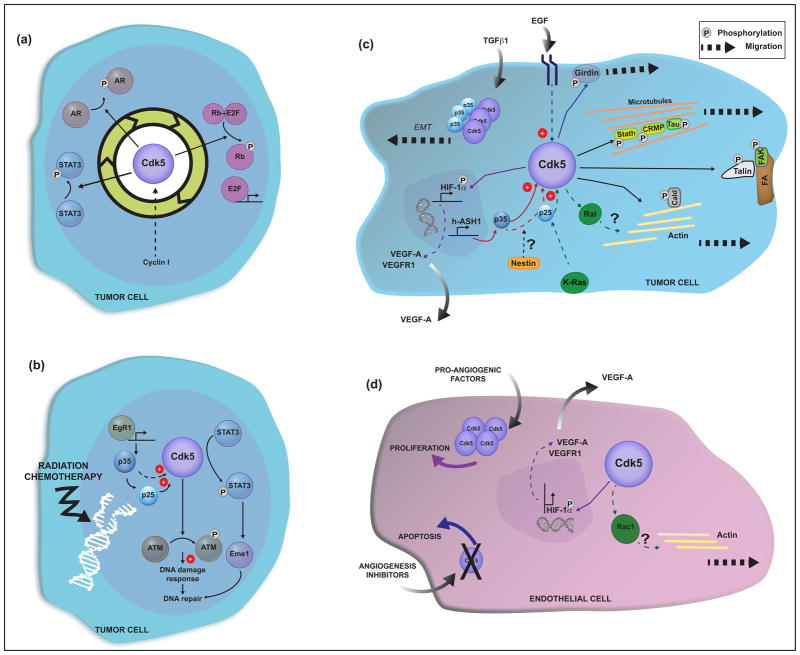
Figure 2. Cdk5-driven mechanisms in cancer progression.
(a) Schematic representation of Cdk5 contribution to cell cycle and proliferation. Cdk5 phosphorylates tumor suppressors and transcription factors involved in cell cycle progression. Cyclin I may bind and activate Cdk5 during the cell cycle. The phases at which Cdk5 regulates each transcription factor have not been clearly defined. (b) Proposed role for Cdk5 in the DNA damage response and DNA repair processes. Cdk5 becomes activated in tumor cells exposed to DNA damaging agents (i.e. radiation and chemotherapy). EgR1 induces p35 expression, which binds and activates Cdk5. P35 can be cleaved to produce p25, which activates Cdk5, as in brain cancers. Upon activation, Cdk5 phosphorylates the checkpoint kinase ATM and the transcription factor STAT3 to transduce DNA damage responses and facilitate DNA repair. (c) Cdk5 in cell motility and migration. Cdk5 becomes activated upon stimulation with TGFβ or EGF and phosphorylates components of the cytoskeleton and focal adhesions to induce cell motility and migration. Cdk5 may facilitate neoplasia and angiogenesis through HIF1α and VEGF signaling. Induction of hAsh1 and subsequent expression of p35 may be a mechanism by which Cdk5 is activated as it occurs in lung cancer. The intermediate filament protein, nestin, is a Cdk5 substrate and might regulate the cleavage of p35-to-p25 by an autoregulatory process. (d) Role of Cdk5 in endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Cdk5 is expressed in endothelial cells, is activated by pro-angiogenic factors and regulates angiogenesis by facilitating the migration of endothelial cells via a Rac-dependent mechanism.
Abbreviations- Retinoblastoma protein (Rb), E2 transcription factor (E2F), androgen receptor (AR), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation (P), early growth response protein (EgR1), Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM), DNA endonuclease (Eme1), human achaete-scute homolog 1 (hASH1), Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF1α), Stathmin (Stath), Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-2 (CRMP), focal adhesions (FA), focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Caldesmon (Cald), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1).