Figure 1.
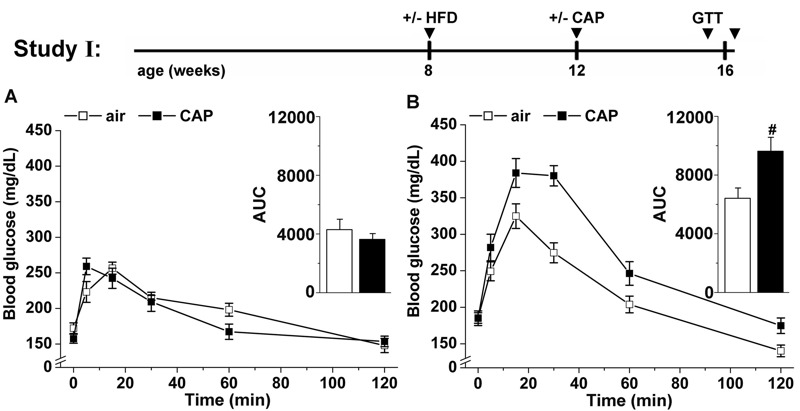
Effects of concentrated fine particulate matter (CAP) exposure on systemic glucose homeostasis. Mice maintained on control diet (13% kcal fat) or placed on a high-fat diet (HFD, 60% kcal fat) were exposed to air or CAP for 30 days (Study I). After 25 days of exposure, systemic glucose tolerance was tested in both control (A) and HFD-fed (B) mice. The total excursion of glucose in the blood was calculated by integrating the area under the curve (AUC, inset). Data are the mean ± SE. # p < 0.05 air versus CAP; n = 8. GTT, glucose tolerance test.
