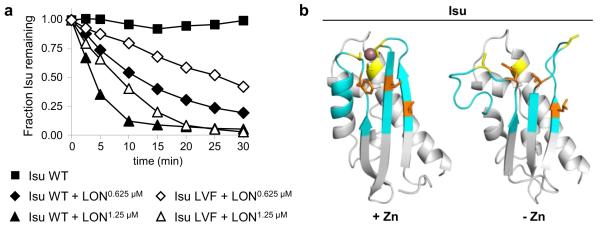
Fig. 2.
Recognition site for Pim1: evidence for a role of the hydrophobic region of Isu that is important for interaction of Nfs1 and Jac1. a Residues Leu63, Val72 and Phe94 form a hydrophobic patch on the surface of Isu, which is a critical part of the interface for both the Nfs1:Isu and Jac1:Isu complexes (Majewska et al. 2013). Using an established in vitro degradation assay (Ciesielski et al. 2016), we examined an Isu variant with serine substitutions of these residues (Isu LVF) to test the importance of this region for recognition of Isu as a Pim1 substrate. Briefly 7.5 μM of purified Isu1 wild type (WT) or Isu1 variant was incubated alone or with one of two different concentrations (0.625 and 1.25 μM) of mitochondrial LON protease, a human homologue of Pim1, in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES–NaOH pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiotreitol, 5 mM ATP, 0.15 mg/ml bovine serum albumin) for 30 min, at 30 °C. At indicated times, aliquots were removed, separated by SDS-PAGE and stained. Amounts of full-length Isu were quantitated by densitometry using ImageJ (Schindelin et al. 2012) and plotted as relative units with the time zero value set at 1. b Similar to Fe–S cluster coordination, binding of a Zn ion engages three evolutionarily conserved cysteine residues of Isu (Iannuzzi et al. 2014). Comparison of models of Zn-bound Isu (left) and apo-Isu (right) showing local structural rearrangement (cyan) in regions containing the LVF residues (orange) involved in Nfs1/Jac1 interaction, and cysteine residues (yellow), involved in zinc ion (purple) coordination. Models of Isu were obtained using SWISS-MODEL server (Bordoli et al. 2009) and visualized using PyMOL (Schrodinger, LLC). For Zn-bound Isu and apo-Isu, NMR solved structures for H. influenza IscU (PDB ID: 1R9P; Ramelot et al. 2004) and E. coli IscU (PDB ID: 2L4X; Kim et al. 2012) were used as templates, respectively. For modeling, Isu lacking the mitochondrial targeting sequence (residues 35–165) was used. In the final model the 16 N-terminal and 7 C-terminal residues are not depicted due to high flexibility of these segments