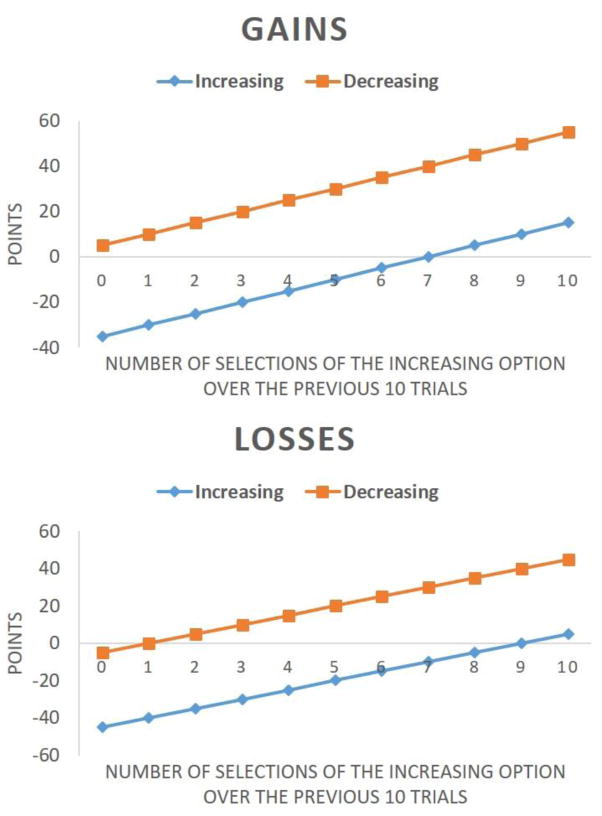
Figure 1.
Point values given as a function of the number of increasing option selections over the previous ten trials in the gains condition (upper panel) and the losses condition (lower panel). In the gains condition, the point value for selecting the increasing option = − 35 + 5h and the point value for selecting the decreasing option = 5 + 5h where h = the number of increasing option selections in the last 10 trials. In the losses condition, the point value for selecting the increasing option = − 45 + 5h and the point value for selecting the decreasing option = − 5 + 5h where h = the number of increasing option selections in the last 10 trials. The point values for the losses condition were derived by subtracting 10 points from each point value in the gains condition. As such, the vertical distances between the two lines are the same across the two conditions, and thus the task is equivalent across the two conditions except whether the end-state of the decreasing option is a gain or loss