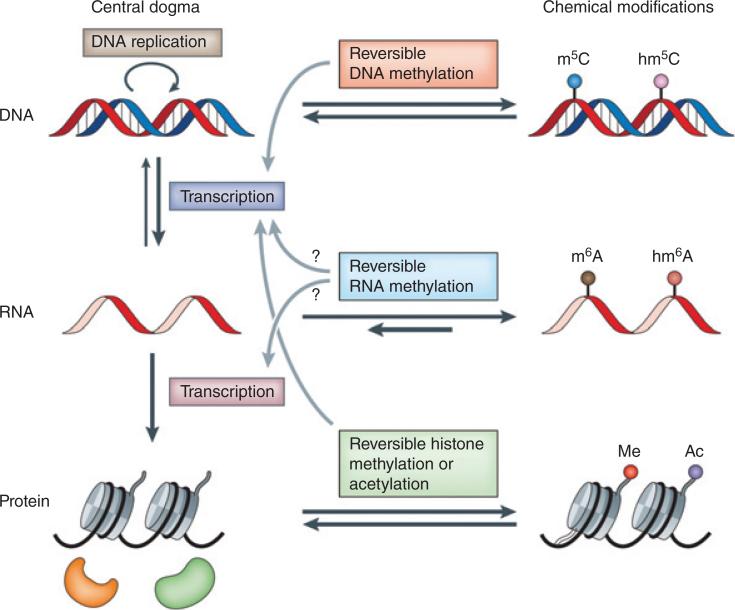
FIGURE 1.
Reversible chemical modifications that regulate the flow of genetic information. In the central dogma, genetic information is passed from DNA to RNA and then to protein. Epigenetic DNA modifications (e.g., the formation of 5-methylcytosine (m5C; also known as 5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hm5C; also known as 5hmC)) and histone modifications (e.g., methylation (me) and acetylation (ac)) are known to have important roles in regulating cell differentiation and development. Reversible RNA modifications (e.g., the formation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and N6-hydroxymethyladenosine (hm6A)) add an additional layer of dynamic regulation of biological processes. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 3. Copyright 2014 Nature Publishing Group)