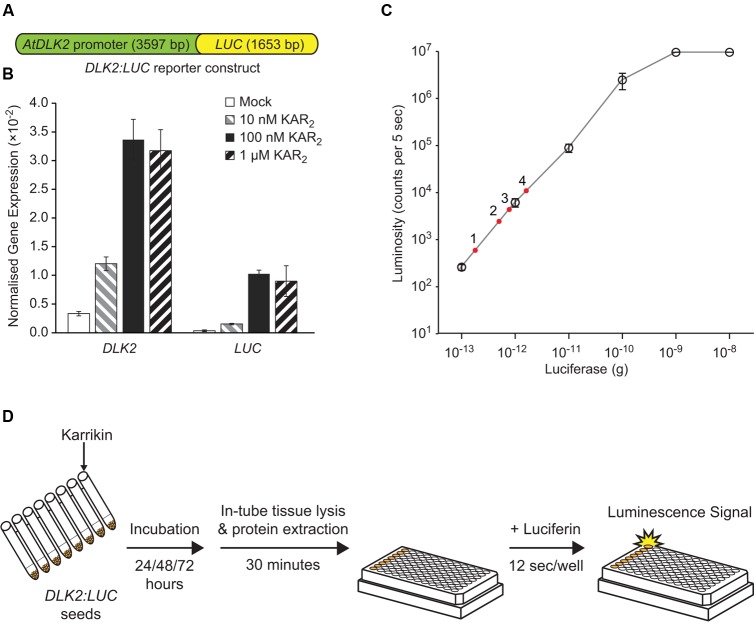
FIGURE 1.
Development of the DLK2:LUC reporter assay. (A) Schematic representation of the DLK2:LUC reporter construct that was transformed to Arabidopsis wild-type Ler (DLK2:LUC [Ler]) and crossed into the karrikin insensitive 2-2 (kai2-2) mutant background (DLK2:LUC [kai2]). The construct contains 3566 bp of intergenic sequence upstream of the transcriptional start site of D14-LIKE 2 (DLK2, At3g24420), 31 bp of DLK2 5′UTR, and 1653 bp of FIREFLY LUCIFERASE (LUC) coding sequence. (B) Response of DLK2 and LUC transcripts to karrikin treatments in DLK2:LUC reporter seeds. Transcript abundance was normalized to CACS (At5g46630). Error bars show standard errors (SE) with n = 3 batches of seeds. In this assay, neither DLK2 nor LUC transcripts could be detected reliably in the DLK2:LUC [kai2] reporter seeds. (C) Standard curve of firefly luciferase enzymatic activity using purified firefly luciferase enzyme and D-luciferin substrate. Error bars show SE with n = 3 experimental replicates, where each dilution was measured with three technical replicates. The red dots represent a typical dataset where luciferase activity in DLK2:LUC [Ler] is induced by (1) mock; (2) 10 nM KAR2; (3) 100 nM KAR2; (4) 1 μM KAR2 over 72 h. (D) Illustration of the DLK2:LUC assay procedure (illustration of the 96-well plate is adapted from Promega’s Technical Bulletin – Luciferase Assay System 12/11).