FIGURE 1.
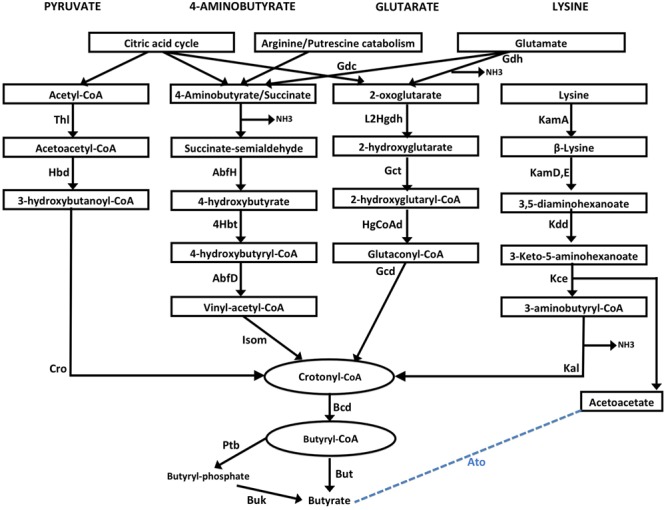
Schematic representation of four butyrate production pathways in bacteria. Pyruvate pathway: Pyruvate is converted to crotonyl CoA using three enzymes, namely, Thiolase (Thl), Hydroxybutyryl dehydrogenase (Hbd) and crotonase/enoyl-CoA hydratase (Cro). 4-aminobutyrate (4Ab) pathway: 4Ab is converted to crotonyl CoA by the action of AbfH (4-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase), 4Hbt (butyryl-CoA:4-hydroxybutyrate-CoA transferase) and AbfD (4-hydroxybutyryl dehydratase) which also possesses vinyl-acetyl-CoA isomerase activity. Glutarate pathway: 2-oxoglutarate conversion to Crotonyl-CoA involves 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase (L2Hgdh), glutaconate-CoA transferase (Gct) and 2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (HgCoAd) and Glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase (Gcd). Glutamate can be converted to 4-aminobutyrate and 2-oxoglutarate by enzymes Glutamate decarboxylase (Gdc) and Glutamate dehydrogenase (Gdh) enzymes. Lysine pathway: Lysine is metabolized to Crotonyl-CoA by lysine 2,3-aminomutase (KamA), lysine 5,6-aminomutase (Kam D,E), 3,5-diaminohexanoate dehydrogenase (Kdd), 3-keto-5-aminohexanoate cleavage enzymes (Kce) and 3-aminobutyryl-CoA ammonia lyase (Kal). Acetoacetate released in the last step can also be converted to Butyate by a few bacteria using butyryl-CoA:acetoacetate-CoA transferase (Ato) enzyme. Crotonyl-CoA, a product from each of the four pathways, is metabolized to butyryl-CoA by butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (Bcd). Conversion of butyryl-CoA to butyrate is catalyzed by either two enzymesphosphate butyryl transferase (Ptb) and Butyrate kinase (Buk), or by butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA transferase (But).
