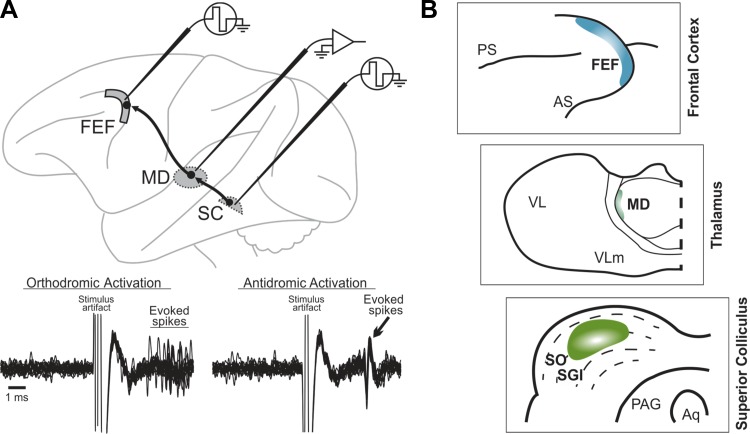
Fig. 1.
Pathway for corollary discharge of saccades. A: electrophysiological identification of the pathway's relay neurons in mediodorsal thalamus (MD). Individual neurons were double-identified as orthodromically activated from the superior colliculus (SC) and antidromically activated from the frontal eye field (FEF). Bottom: traces show repeated, superimposed recording traces of an example MD neuron. Just after stimulation of the SC (left), the neuron fired with a variable latency. The same neuron showed a consistent latency of activation from the FEF (right). B: schematics depicting a close-up of the target of the pathway adapted from Lynch et al. (1994) with permission of Springer: the FEF (top); the relay zone at the lateral edge of MD (middle); and the source zone in the intermediate SC (bottom). PS, principal sulcus; AS, arcuate sulcus; VL, ventrolateral nucleus; VLm, ventrolateral nucleus pars medialis; SO, stratum opticum; SGI, stratum griseum intermedium; PAG, periaqueductal gray; Aq, cerebral aqueduct.