Fig. 1.
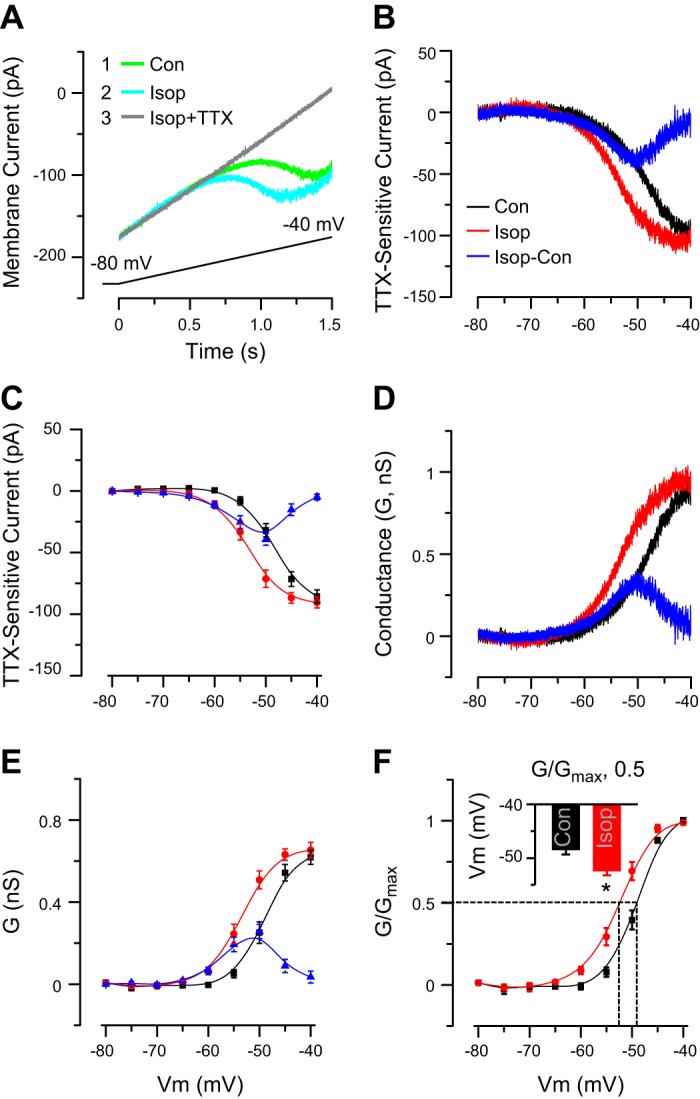
Isop enhances INaP. A: example ET cell voltage-clamp recording shows that a slow depolarizing voltage ramp (from −80 mV to −40 mV, shown at bottom, 26.6 mV/s) elicits an INaP (Isop, 10 μM). Inset indicates order of drug applications. INaP was activated in the middle of the ramp (A) or at approximately −60 mV (as shown in B and C) and was TTX sensitive. Con, control. B: example subtraction I-V curves (from cell in A) show TTX-sensitive INaP in control and Isop. Blue curve shows the net increase in INaP induced by Isop. C: group data from 5 ET cells show TTX-sensitive current INaP in control and Isop and the net change of INaP induced by Isop (Isop-sensitive INaP). Note leftward shift of I-V curve with a decrease in INaP activation threshold and increased INaP amplitude from −60 mV to −45 mV evoked by Isop. D: I-V curves for INaP (in B) were converted to conductance. E: group data from 5 ET cells show INaP conductance in control and Isop treatment and the net change induced by Isop. Isop induced a leftward shift in conductance-voltage curve and increased the INaP conductance. F: group data from 5 ET cells show the G/Gmax-V relationship in control and Isop. Note leftward shift induced by Isop. Dashed lines denote half-maximal activation values in control and Isop. Inset shows that Isop had a more negative membrane potential (Vm) at half-maximal activation. *P < 0.01 vs. control, paired t-test.
