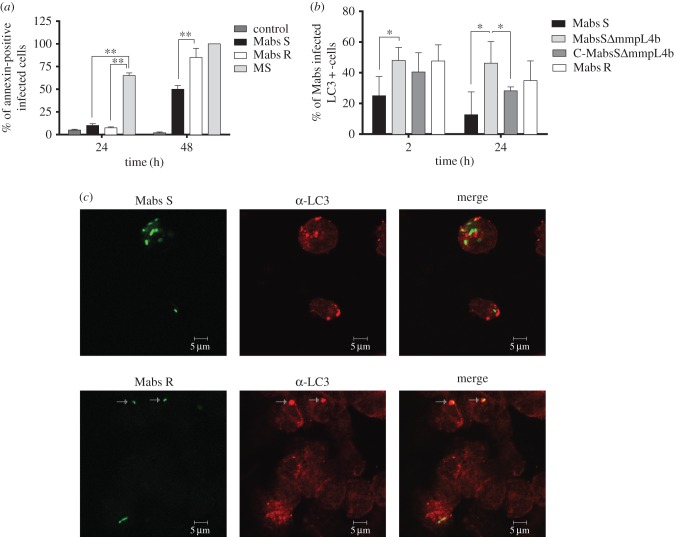
Figure 6.
Mycobacterium abscessus-induced apoptosis and autophagy in wild-type Mϕ. (a) Analysis of apoptosis: THP-1 Mϕ were infected with M. abscessus S (Mabs S), M. abscessus R (Mabs R) or M. smegmatis (MS). The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined at 24 h p.i. using annexin-V-FITC conjugates (Abcam, USA) and propidium iodide to stain the dead cells. Fluorescent signals (mCherry from mycobacteria, FITC from the annexin-V and absence of propidium iodide) were analysed by flow cytometry. A significant increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells was associated with M. smegmatis-infected cells when compared with Mϕ infected with M. abscessus S or R. However, the R variant was significantly more pro-apoptotic than the S variant at 48 h. Error bars indicate the s.e.m. based on the results of two independent experiments (**p < 0.01). (b,c) Comparative behaviour of M. abscessus S and R variants towards autophagy. (b) Percentage of colocalization of M. abscessus S (Mabs S), S ΔmmpL4b mutant (MabsS ΔmmpL4b), ΔmmpL4b complemented (C-MabsS ΔmmpL4b) and R (Mabs R)-infected cells with LC3 at 2 and 24 h p.i. determined after immunofluorescence analyses. Error bars indicate the s.e.m. based on the results from four independent experiments (*p < 0.05). (c) Confocal immunofluorescence images of fixed THP-1 cells infected with Alexa-488-labelled M. abscessus variant S (Mabs S) or variant R (Mabs R) (green) (2 h p.i.) and immuno-stained for endogenous LC3 (red). Scale bars, 5 µm.