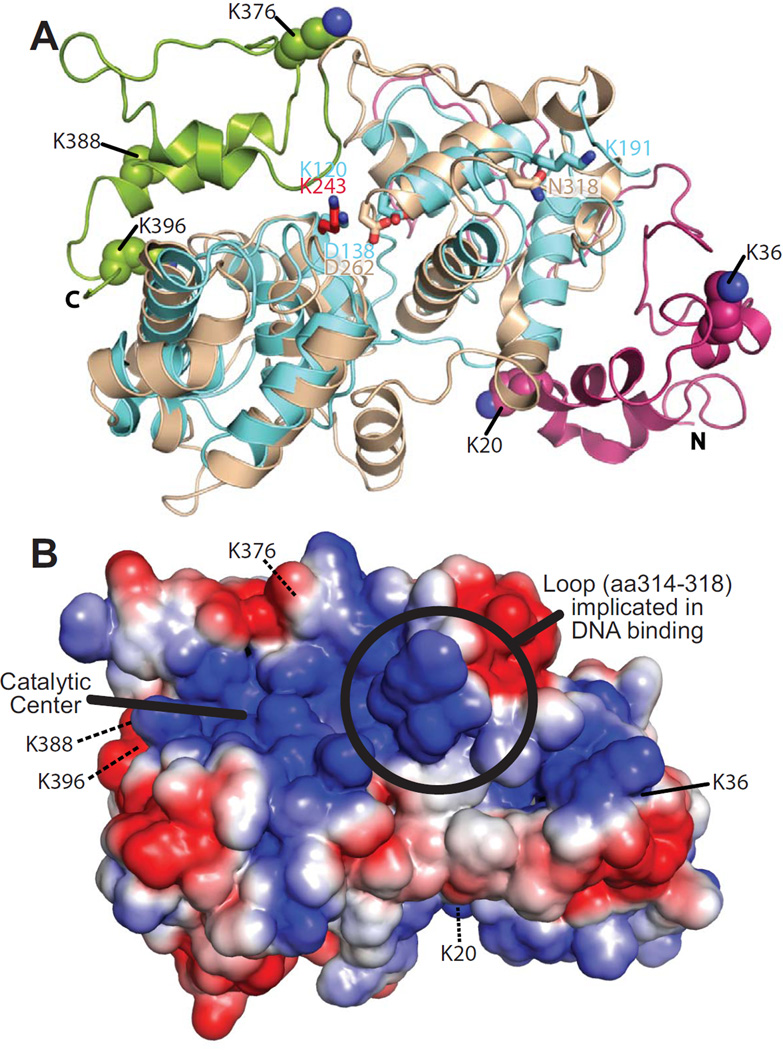
Figure 3. Homlogy model of Ntg1.
A. A homology model of Ntg1 shown as a ribbon diagram was generated as described in Materials and Methods. The model is overlaid on the E. coli Ntg1 homologue, Endonuclease III, structure (cyan, PDB ID: 2ABK). The Ntg1 catalytic domain (amino acids 95–335; tan), N-terminal domain (amino acids 1–94; magenta), C-terminal domain (amino acids 336–399; green), catalytic amino acid of Ntg1 (K243, red) and Endonuclease III (K120, blue) are shown in addition to Endonuclease III amino acids D138, important for catalysis, and K191, implicated in DNA binding (69), and the corresponding amino acids in Ntg1 (D262 and N318, respectively). The five consensus sumoylation sites (K20, K38, K376, K388, and K396) are shown as balls and indicated by the labeling. B. An electrostatic model of Ntg1 is shown based on the homology model. Positive and negative residues are colored in blue and red, respectively. White indicates neutral residues. The loop containing residues 314–318, indicated by a circle, has been implicated in DNA binding by Endo III (69). The catalytic center is indicated by a bold black line and the five consensus sumoylation sites are labeled and indicated by black lines. Residues 20, 376, 388, and 396 are located on the back face of the model and are indicated by black dotted lines.