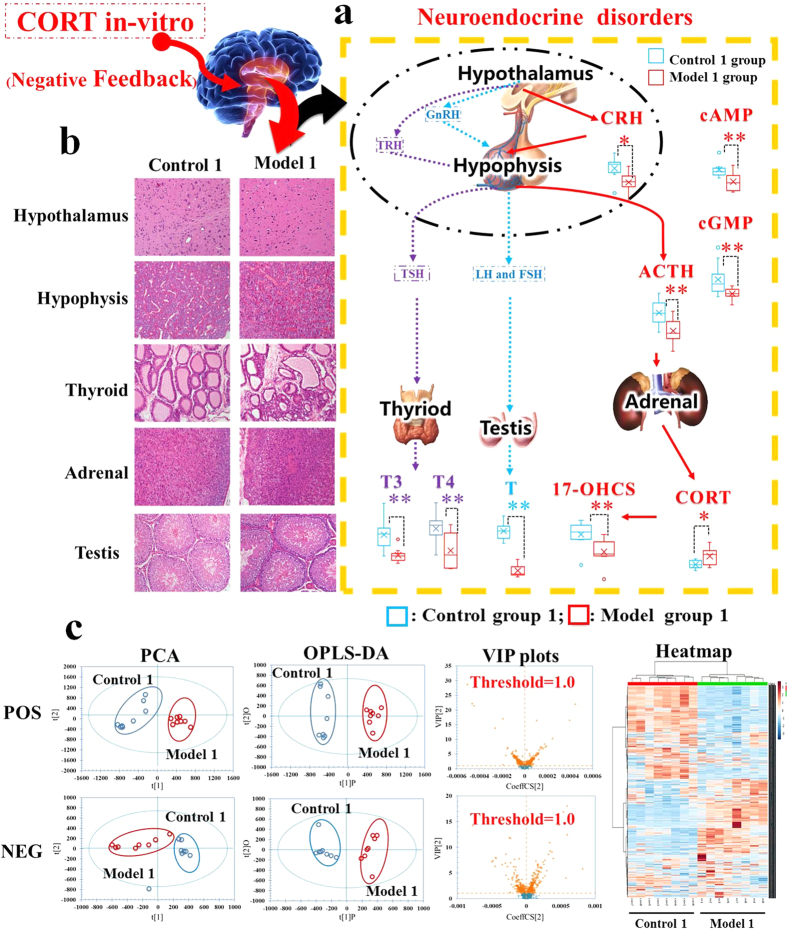
Figure 1. The evaluation system diagrams of Kidney-Yang Deficiency Syndrome related to neuroendocrine hypofunction (day 22).
(a) H&E staining for histological evaluation. The pictures of KYDS model rats showed that the number of depauperate hypothalamic neurons was reduced, the counts of basophilic cells in hypophysis was decreased, the atrophic adrenocorticals were found by observing thinning of the cortex, the thyroid follicules were atrophic, deformed, and the interstitial fibrous matter around the thyroid follicules were proliferated therein. (b) The biochemical characteristics for evaluation of neuroendocrine system. Significant changes in the concentrations of CRH, ACTH, 17-OHCS, T3, T4, T, cAMP, and cGMP were decreased in KYDS model rats (Student’s t-test; *significant difference from control group 1 at p < 0.05, **significant difference from control group 1 at p < 0.01). (c) Multivariate data analyses resulting from the UPLC/MS spectra of serum samples. Score plots of PCA discriminated control group 1 and model group1, then score plots of VIP analysed by OPLS-DA extracted the significant contribution of different ions to the separation between control group 1 and model group1 rats. Meanwhile, a heat-map of the metabolites in two groups was derived from MetaboAnalyst 3.0 software, which exhibited a significant difference between control group 1 and model group1 rats.