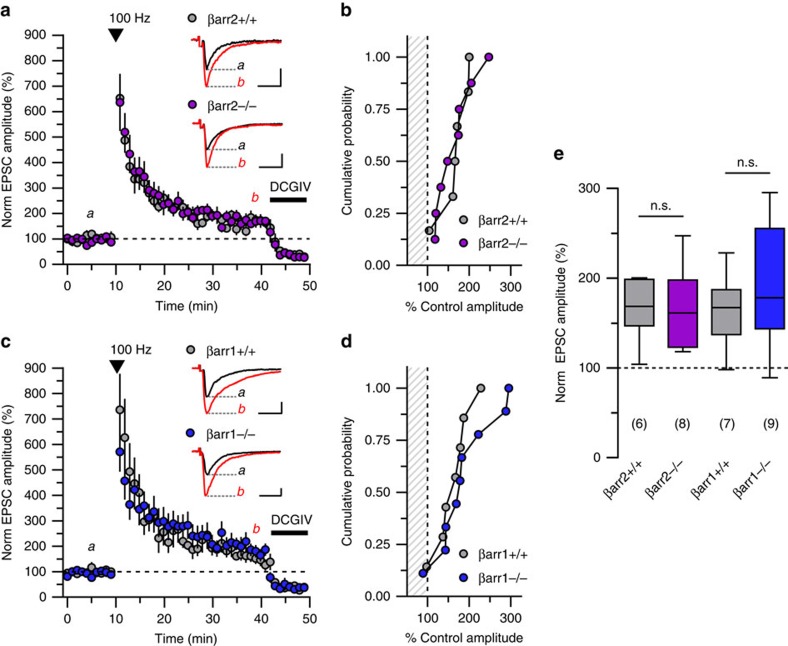
Figure 3. Classical mossy fibre LTP does not require β-arrestins.
(a,b) High-frequency stimulation (HFS) of mossy fibre inputs elicits robust potentiation of mfEPSCs in slice recordings from both βarr2−/− and βarr2+/+ mice (P=0.85, n=6 cells from three wild-type animals, n=8 cells from five knockout animals). A time course plot and cumulative probability histogram illustrate robust facilitation following HFS (amplitudes during HFS were omitted). Amplitudes deprecate over time but remain elevated relative to baseline 25–30 min post-tetanus. (c,d) mfLTP is intact in βarr1−/− mice. mfEPSC amplitudes measured from βarr1+/+ and βarr1−/− mice are strongly potentiated immediately following tetanus and slowly deprecate to similar levels above baseline 30 min later (P=0.56, n=7 cells from six wild-type animals, n=9 cells from eight knockout animals). Individual post-train measurements are provided in a cumulative probability histogram. (e) mfLTP potentiation levels in β-arrestin knockout mice and wild-type littermates are summarized by a box plot and 10–90th percentile whiskers. Representative trace calibration: x axes, 10 ms; y axes, 250 pA. Groups were compared by Mann–Whitney tests; n.s., non-significant.