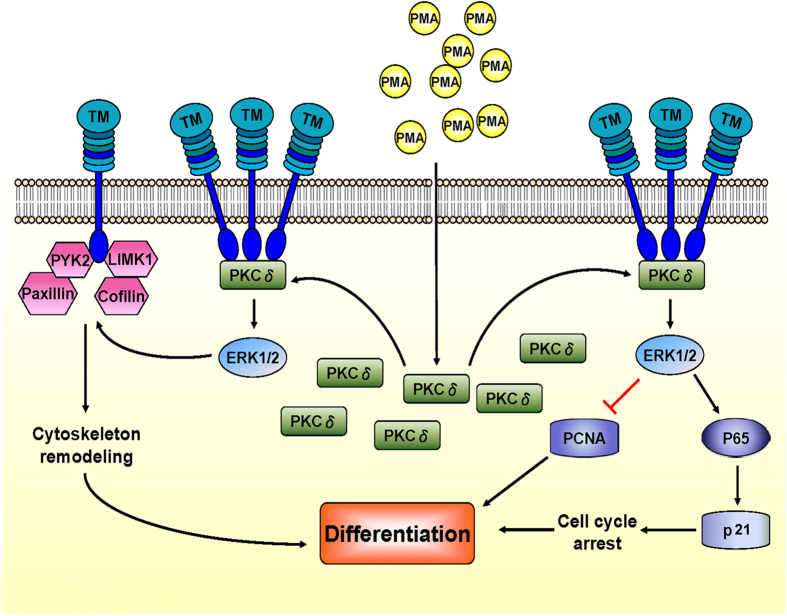
Figure 7. Mechanism by which TM contributes to PMA-mediated differentiation in THP-1 cells.
TM expression is increased soon after PMA induction in THP-1 cells. TM may regulate PMA-induced THP-1 cell differentiation via a direct interaction with PKCδ. TM acts as a scaffold for PKCδ docking, which keeps PKCδ in the region close to the membrane and promotes subsequent ERK1/2 activation. ERK1/2 activation subsequently enhances the expression of cell cycle inhibitor p21Cip1/WAF1 via NF-kB p65 signaling, which causes cell cycle arrest and promotes differentiation. On the other hand, ERK1/2 activation participates in the phosphorylation of paxillin, cofilin, LIMK1, and PYK2, which interact with TM and mediate cytoskeleton remodeling to promote differentiation.