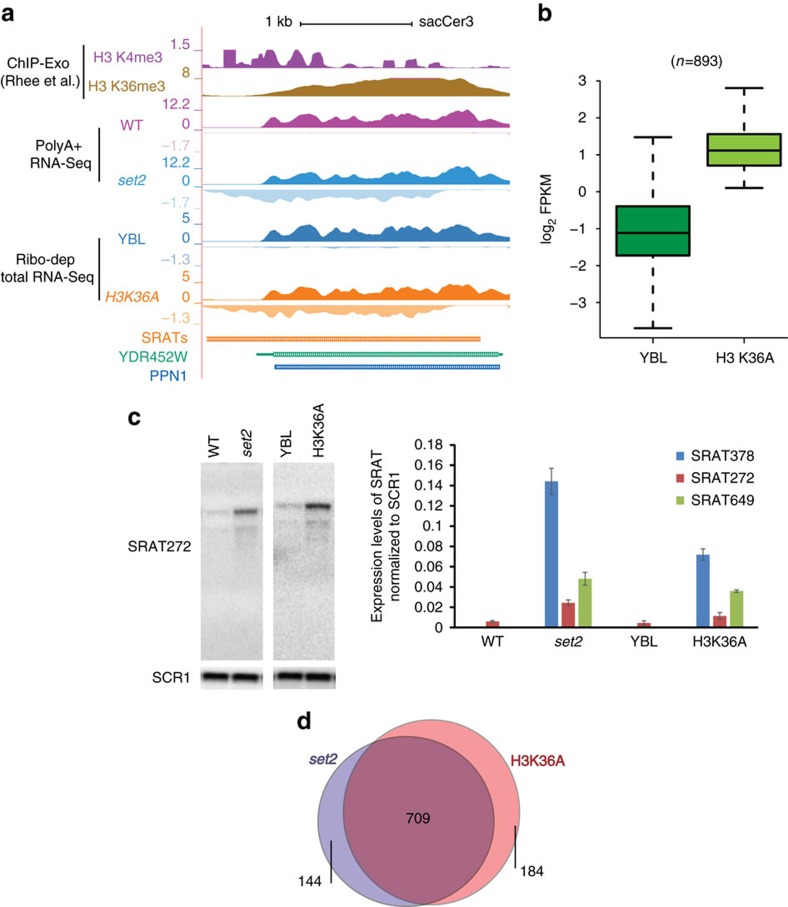
Figure 2. Loss of H3K36 methylation de-represses SRAT production.
(a) Genome browser profile showing the histone modifications and transcripts (poly A+ and ribodepleted) produced in wild-type strain (WT, YBL) and the SET2 (set2) and H3K36A mutants (H3K36A) over the gene YDR452W (PPN1). Each track, an amalgamation of two biological repeats, is separated into the sense strand (S) on top, running from left to right and the antisense strand (AS) in the bottom running from right to left. The H3K36A mutant produces the antisense transcript, SRAT282, as observed in the set2 mutant. (b) Boxplot showing the abundance of significant SRATs (log2 FPKM) in the WT (YBL) and H3K36A mutant. The total number of SRATs used in the analysis is denoted above the plot. (c) (Left) Strand-specific northern blot probing for SRAT282 using total RNA in either the respective wild-type (WT-BY4741 or YBL), SET2 deletion mutant (set2) and the H3K36A mutant strain. SCR1 is used as a loading control. (Right) Quantitation of strand-specific northern blots indicating the expression level of selected SRATs, normalized to the level of SCR1 in total RNA in the indicated mutants. Error bars denote the s.e.m. of three to four independent repeats. (d) Venn diagram showing the overlap of statistically significant SRATs produced upon deletion of SET2 (set2) with those in an H3K36A point mutant.