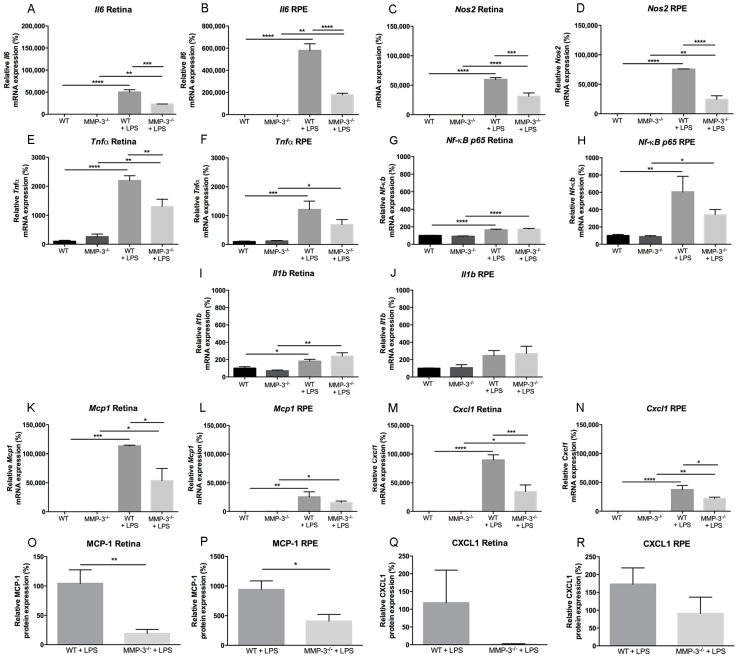
Figure 5.
MMP-3 deficiency prevents strong upregulation of inflammatory-associated molecules in the retina and RPE during EIU. (A–N) The gene expression levels of interleukin 6 (Il6), nitric oxide synthase (Nos2), tumor necrosis factor alpha (Tnfα), nuclear factor kappa B p65 subunit (Nf-κB p65), Il1b and monocyte chemoattractant protein (Mcp1/Ccl2), (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (Cxcl1) were performed on WT and MMP-3−/− retinal and RPE samples at 0 and 16 hpi. Healthy retina and RPE samples from WT and MMP-3−/− mice showed very low to undetectable mRNA levels. Most of the inflammatory genes, i.e., Il6 (A,B), Nos2 (C,D), Tnfα (E,F), Mcp1 (K,L) and Cxcl1 (M,N) were significantly upregulated in WT eyes subjected to EIU (16 hpi), and to a much lesser extent, in the MMP-3−/− retina and RPE; Nf-κB p65 (G,H) is predominantly upregulated in the RPE, and MMP-3 deficiency reduces its levels in the RPE, yet not significantly; Il1b (I,J) showed only a limited upregulation in WT and MMP-3−/− retinal and RPE samples subjected to EIU, and no clear difference was revealed between WT and MMP-3−/− mice after LPS. For most of the inflammatory molecules, the highest increase in mRNA levels, as well as the most pronounced difference between the WT and MMP-3−/− condition, is observed in the RPE. RT-PCR data were normalized against the reference genes and were expressed as a percentage relative to 0 hpi (n ≥ 3); (O–R) Retinal and RPE samples from WT and MMP-3−/− mice with or without LPS injection were also analyzed for the pro-inflammatory chemokines MCP-1 (O,P) and CXCL1 (Q,R) at the protein level via cytometric bead array at 16 hpi. Levels of both MCP-1 and CXCL1 are significantly upregulated after EIU in WT mice and MMP-3 deficiency clearly suppressed this augmentation, especially the MCP-1 protein levels. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n ≥ 5, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001 and **** p ≤ 0.0001. Data with no indicated statistical analysis point out no significant results.